How Inositol Reduces PCOS Inflammation
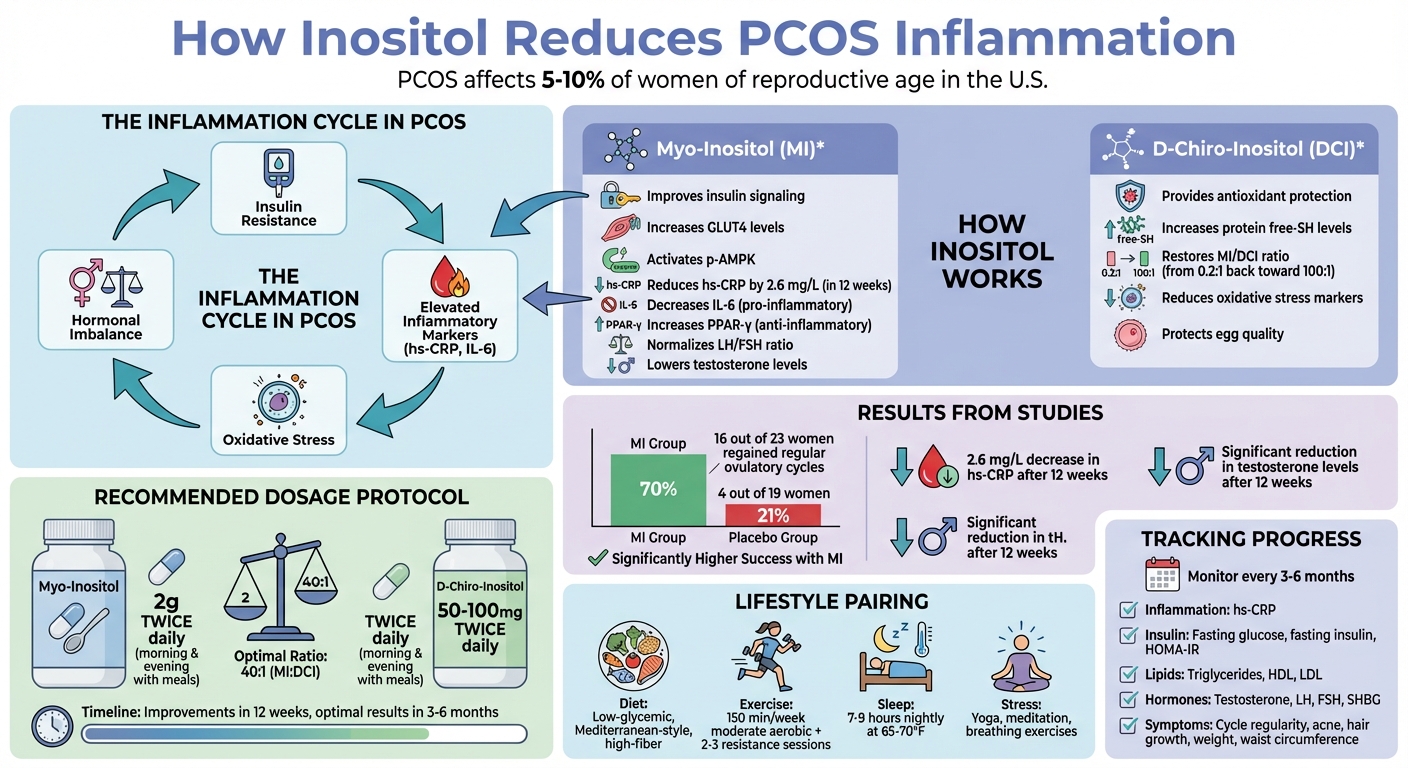
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) affects 5-10% of women of reproductive age in the U.S., often causing irregular periods, high androgen levels, and insulin resistance. Chronic inflammation plays a key role in worsening these symptoms, but inositol, a natural supplement, can help reduce inflammation and improve metabolic and hormonal health.
Key Takeaways:
- Inflammation in PCOS: Caused by elevated markers like hs-CRP and IL-6, driven by insulin resistance and oxidative stress.
- What Inositol Does: Improves insulin sensitivity, reduces oxidative stress, and balances hormones.
- Myo-inositol (MI): Enhances insulin signaling, lowers inflammation markers, and improves egg quality.
- D-chiro-inositol (DCI): Reduces oxidative stress and supports ovarian health.
- Dosage: A 40:1 ratio of MI (2g twice daily) to DCI (50–100mg twice daily) is recommended for best results.
- Lifestyle Pairing: A low-glycemic diet, regular exercise, stress management, and adequate sleep enhance inositol's effects.
Inositol is a safe, effective option for managing PCOS-related inflammation and improving overall hormonal balance when combined with healthy lifestyle changes. Regular monitoring of symptoms and lab markers can track progress over time.
How Inositol Reduces PCOS Inflammation: Mechanisms and Treatment Protocol
Inositol: The Most Underrated Supplement for PCOS
How Inositol Reduces Inflammation in PCOS
Inositol helps manage inflammation in PCOS by improving insulin sensitivity and reducing oxidative stress, effectively disrupting the cycle of inflammation.
Improving Insulin Sensitivity
Myo-inositol plays a key role in enhancing insulin signaling. It works by increasing essential second messengers and boosting GLUT4 levels, which improves glucose uptake. This, in turn, leads to lower circulating insulin levels and a reduction in inflammatory markers. For instance, a 2017 randomized controlled trial revealed that women with PCOS who took myo-inositol for 12 weeks experienced a 2.6 mg/L decrease in high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP), a marker of systemic inflammation.
Additionally, myo-inositol activates p-AMPK in both endometrial and ovarian cells. This activation restores glucose uptake and GLUT4 levels, mimicking the effects of metformin on glucose metabolism. By influencing inflammatory pathways - such as reducing pro-inflammatory IL-6 and increasing anti-inflammatory PPAR-γ - myo-inositol helps create a metabolic environment that is less prone to inflammation. While enhancing insulin function is a major step, addressing oxidative stress is equally important for reducing inflammation in PCOS.
Reducing Oxidative Stress
Beyond improving insulin sensitivity, D-chiro-inositol (DCI) provides antioxidant benefits that protect ovarian tissues from oxidative damage. This damage, if unchecked, can harm egg quality and trigger inflammation. Research shows that DCI increases protein free-SH levels in follicular fluid, which is a marker of antioxidant capacity.
In PCOS, the typical MI/DCI ratio of about 100:1 shifts drastically to around 0.2:1, creating an oxidative environment that disrupts egg development and promotes inflammation. Supplementing with DCI helps restore this balance, reducing oxidative stress markers and improving the health of the follicular environment. Studies also suggest that DCI supplementation may help lower BMI and replicate some of metformin's effects by combating oxidative stress.
How Inositol Supports Hormonal Balance
Inositol plays a key role in improving insulin sensitivity and stabilizing hormonal signaling, which helps break the cycle of high androgens and disrupted ovulation often linked to inflammation. These hormonal shifts contribute to reducing inflammation associated with PCOS.
Normalizing LH and FSH Levels
Women with PCOS frequently experience an imbalanced LH/FSH ratio, often tied to hyperinsulinemia and ovarian dysfunction. Myo-inositol, a precursor to inositol triphosphate, aids in effective FSH and insulin signaling. This process helps restore the LH/FSH balance and decreases inflammatory cytokines like interleukin-6.
One study highlighted the impact of myo-inositol supplementation: women taking 2 grams daily for 12 weeks saw significant results, with 16 out of 23 participants regaining regular ovulatory cycles compared to just 4 out of 19 in the placebo group.
Lowering Androgen Levels
High androgen levels, such as testosterone and androstenedione, are common in PCOS and can lead to inflammation, acne, and excess facial hair. Inositol improves insulin sensitivity by enhancing GLUT4 activity and activating AMPK, which reduces ovarian theca cell production of androgens.
Research, including meta-analyses, shows that 12 weeks of myo-inositol supplementation significantly lowers serum testosterone. Combining myo-inositol (MI) with D-chiro-inositol (DCI) further amplifies these benefits. Lower androgen levels not only decrease sebum production and follicular stimulation but also reduce oxidative stress and inflammatory markers.
sbb-itb-6dba428
How to Use Inositol for PCOS Management
Incorporating inositol into your approach to managing PCOS calls for a well-thought-out plan. The right dosage, combined with healthy lifestyle choices and regular monitoring, can help address hormonal imbalances and reduce inflammation.
Recommended Dosage and Duration
Research suggests taking myo-inositol 2 g twice daily along with D-chiro-inositol 50–100 mg twice daily, maintaining a 40:1 MI:DCI ratio for optimal results. This specific ratio supports better insulin sensitivity and ovarian function while avoiding potential side effects linked to higher doses of D-chiro-inositol.
It's best to take these doses with meals - once in the morning and once in the evening - for improved tolerance and steady blood sugar levels. If you experience stomach discomfort, start with a smaller dose (1–2 g daily) for a few days before increasing to the full amount. Many people notice improvements in inflammation markers within 12 weeks, with more noticeable symptom relief - such as regular periods, clearer skin, and reduced excess hair - occurring after 3–6 months of consistent use.
Combining Inositol with Lifestyle Changes
For inositol to work most effectively, it should be paired with supportive lifestyle habits. A moderate-carbohydrate, high-fiber, low-glycemic diet can significantly enhance its benefits. Include foods like non-starchy vegetables, whole grains, legumes, lean proteins (such as chicken or fish), and healthy fats from sources like olive oil and nuts. Limiting added sugars and processed foods can further improve insulin sensitivity and reduce inflammation. A Mediterranean-style diet - featuring salmon, beans, and plenty of vegetables - pairs particularly well with inositol for managing PCOS symptoms.
Regular physical activity is another key component. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week (like brisk walking, cycling, or swimming) and include 2–3 resistance training sessions targeting major muscle groups. Short walks after meals can also help stabilize blood sugar levels and enhance the effects of inositol. Managing stress and prioritizing quality sleep are equally important. Chronic stress raises cortisol levels, which can worsen insulin resistance, while 7–9 hours of sleep per night in a cool room (around 65–70°F) may help lower inflammation. Practices like yoga, mindfulness meditation, or paced breathing can further support a balanced metabolism.
Tracking Your Progress
To make the most of your PCOS management plan, keeping track of your progress is essential. Work with your healthcare provider to monitor critical lab markers every 3–6 months, including:
- Inflammation: high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP)
- Glycemic control and insulin resistance: fasting glucose, fasting insulin, and HOMA-IR
- Lipid profile: triglycerides, HDL, and LDL levels
- Reproductive hormones: total and free testosterone, LH, FSH, and SHBG
At home, use tools like a cycle-tracking app to log menstrual cycle patterns, ovulation test results, and bleeding details. Keeping a symptom journal can help you note changes in acne, facial hair, scalp hair loss, mood, and energy levels. Regularly track your weight (in pounds) and waist circumference (in inches), and consider monitoring blood pressure if needed. Reassess your progress after 12 weeks and again at 6 months to decide whether to continue with your current plan, adjust your dosage, or explore other treatment options.
For tailored advice, consider consulting a healthcare professional through Oana Health's telehealth services (https://oanahealth.com).
Conclusion
Inositol provides a multi-faceted approach to tackling PCOS-related inflammation by targeting key hormonal and metabolic imbalances. One of its primary benefits is improving insulin sensitivity, which helps reduce hyperinsulinemia - a major factor in the production of inflammatory cytokines. Studies have shown noticeable decreases in inflammatory markers within just 12 weeks of use.
In addition to its effects on insulin, inositol supports hormonal balance through its antioxidant properties. By reducing oxidative stress in ovarian tissues, it promotes healthier hormone levels and improves egg quality. This combination of benefits helps lower inflammation, regulate LH/FSH ratios, and decrease androgen levels, which can lead to more regular menstrual cycles and improved ovulation.
While inositol is both safe and effective, individual results can vary. When paired with a lifestyle that includes nutritious eating, regular physical activity, effective stress management, and adequate rest, inositol becomes a key part of a well-rounded strategy for managing PCOS. Its ability to address the underlying inflammation highlights its importance in reducing many of the complications associated with the condition.
For tailored advice and treatment, consider consulting a healthcare provider who specializes in PCOS. Services like Oana Health’s telehealth platform offer personalized, evidence-based treatment plans designed to address insulin resistance, hormonal imbalances, and other PCOS-related challenges - all delivered straight to your home.
FAQs
How does inositol help reduce insulin resistance and inflammation in women with PCOS?
Inositol offers valuable support for women with PCOS by improving the way their bodies handle insulin. It works by boosting the activity of insulin receptors, helping cells absorb glucose more effectively and reducing insulin resistance. This can stabilize blood sugar levels and promote hormonal balance, which may also help reduce inflammation often associated with PCOS.
By tackling insulin resistance, inositol can help ease common PCOS symptoms such as irregular periods, acne, and difficulties with weight management. It's a helpful option for managing the challenges that come with PCOS.
What side effects can inositol cause when used for managing PCOS?
Inositol is usually easy on the system, but some individuals might notice mild side effects. These could include nausea, bloating, or diarrhea. On rare occasions, it might cause dizziness or trigger allergic reactions.
For safe use and to find the right dosage, it's smart to check in with a healthcare provider - especially if you're dealing with PCOS or other medical conditions.
Can inositol help manage PCOS symptoms on its own, or are lifestyle changes also needed?
Inositol is known to help support hormonal balance and reduce inflammation linked to PCOS. But its effectiveness often increases when paired with healthy lifestyle choices, like eating a balanced diet, staying active, and managing stress.
Although inositol supplements can provide noticeable benefits, tackling PCOS typically calls for a well-rounded approach that fits your unique needs. By combining inositol with lifestyle changes, you may see better results in managing symptoms such as insulin resistance, hormonal disruptions, and inflammation.
