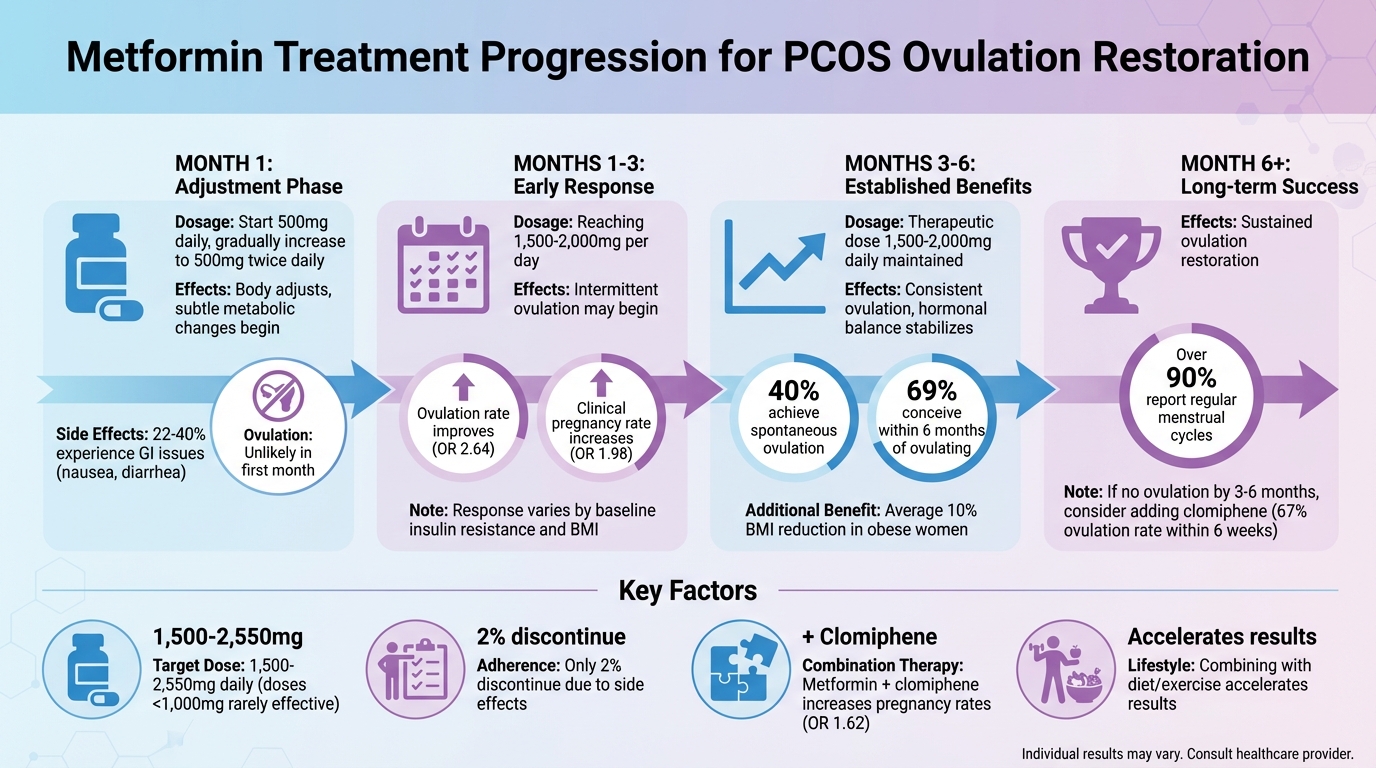
Metformin Treatment Duration: Impact on Ovulation
Metformin can help women with PCOS restore ovulation by addressing insulin resistance - a key factor in the hormonal imbalance that disrupts ovulation. Here’s what you need to know:
- How it works: Metformin reduces insulin levels, which helps lower testosterone and supports normal follicle development.
- Timeline: Changes may start within 3–4 weeks, but consistent use for 4–6 months is typically needed for ovulation to resume.
- Success rates: Over 90% of women report regular menstrual cycles after 6 months of treatment. Around 69% conceive within six months of ovulating.
- Dosage: The most effective range is 1,500–2,000 mg per day, gradually increased to minimize side effects.
- Side effects: Gastrointestinal issues like nausea are common but can be managed by starting with a low dose and taking it with meals.
If ovulation doesn’t occur after 3–6 months, combining metformin with medications like clomiphene may improve outcomes. For those struggling with side effects, extended-release or topical formulations are available. Consistency is key - metformin works best when taken regularly over time.
Metformin Treatment Timeline for PCOS Ovulation Restoration
Can women with PCOS,regular cycles & taking metformin become pregnant? - Dr. Shailaja N
Metformin's Effects on Ovulation in the First Month
When starting metformin, the first 30 days are less about restoring ovulation and more about helping the body adjust to the medication. During this time, metformin begins its work by reducing glucose production in the liver and improving insulin sensitivity. However, these changes are subtle and usually don't result in ovulation right away. Instead, this period is focused on gradually increasing the dosage to ensure the body tolerates it well.
Treatment typically starts with 500 mg taken once daily alongside a main meal during the first week. The dose is then gradually increased to 500 mg twice daily. This step-by-step approach helps reduce common gastrointestinal side effects like nausea and diarrhea, which affect 22–40% of users. It's worth noting that doses below 1,000 mg per day are generally less effective, and it can take several weeks to reach the target range of 1,500–2,000 mg per day.
While metformin begins to lower insulin levels relatively quickly, achieving ovulation requires more time. Sustained metabolic improvements, such as reduced testosterone levels and proper follicle development, are necessary. Research shows that consistent treatment over several months is needed to regulate ovulation. In fact, guidance from leading U.S. medical centers suggests it may take up to six months for menstrual cycles to normalize.
During this early phase, healthcare providers prioritize monitoring how well the medication is tolerated and adjusting the dosage rather than focusing on ovulation tracking. Because ovulation might occur unpredictably before menstrual cycles become regular, effective contraception is recommended if pregnancy is not the goal. On the other hand, for those aiming to conceive, having regular intercourse every 2–3 days is advised, as pinpointing ovulation timing can be challenging in the initial weeks.
Metformin's Effects on Ovulation at 1–3 Months
Between the first and third months of treatment, metformin starts to restore ovulation in many women. During this time, intermittent ovulation often occurs as the medication begins to reduce insulin resistance and lower androgen levels. This process typically coincides with reaching therapeutic doses of 1,500–2,000 mg per day.
Clinical studies reveal that metformin significantly enhances ovulation rates (OR 2.64, 95% CI 1.85–3.75) and clinical pregnancy rates (OR 1.98, 95% CI 1.47–2.65) within this timeframe. Notably, many ovulatory cycles contributing to these outcomes happen during the first three months, particularly in women with milder insulin resistance. These findings highlight how individual factors can influence how quickly patients respond to treatment.
Response rates vary depending on patient characteristics. Women with less severe obesity, lower baseline testosterone levels, and milder insulin resistance often resume ovulation earlier in this period. Additionally, combining metformin with lifestyle changes - like moderate weight loss and increased physical activity - can accelerate improvements. On the other hand, women with severe obesity or a history of long-term anovulation may require a longer treatment period or additional interventions.
Benefits from metformin often become more noticeable after about eight weeks of consistent use. Educational materials in the U.S. note that while some women may see improvements in cycle regularity around the three-month mark, full regulation of menstrual cycles might take up to six months. During this phase, healthcare providers may recommend tracking menstrual cycles and using mid-luteal progesterone tests to confirm ovulation.
If ovulation has not occurred by the end of three months at a therapeutic dose, clinicians often reassess adherence and consider adding ovulation-induction medications like clomiphene. Research shows that combining metformin with clomiphene results in higher clinical pregnancy rates compared to using clomiphene alone (OR 1.62, 95% CI 1.32–1.99). Telehealth platforms like Oana Health can assist during this critical period by remotely adjusting prescriptions and offering follow-up counseling. The next section will explore how metformin continues to impact ovulation beyond the three-month mark and the advantages of extended therapy.
Metformin's Effects on Ovulation at 3-6+ Months
Continuing metformin treatment for more than three months delivers progressive benefits in restoring ovulation. This happens because it takes time for insulin resistance and testosterone levels to decrease and stabilize. These gradual improvements highlight the importance of sticking with the treatment for an extended period.
Beyond restoring ovulation, long-term metformin use also boosts chances of conception. By allowing hormones to balance over time, it creates an environment that supports both ovulation and successful pregnancy outcomes.
The most effective dosage typically falls between 1,500–2,000 mg per day, a level usually achieved within four to six months of treatment. Women with obesity may see even greater benefits during this period, including an average 10% reduction in BMI, which further improves reproductive health. Studies show that consistent metformin use significantly enhances ovulation rates (OR 2.64, 95% CI 1.85–3.75) and clinical pregnancy rates (OR 1.98, 95% CI 1.47–2.65).
For some, gastrointestinal side effects can make it harder to stick with the treatment. However, maintaining consistency is crucial for long-term success. In one study, only 2% of patients stopped taking metformin due to these side effects, while 10% needed to lower their dose. For those struggling with oral metformin, alternative options like topical formulations are available. For example, Oana Health offers topical metformin, which can provide similar benefits with fewer side effects, making it easier for patients to stay on track.
If ovulation doesn’t occur after extended treatment, adding clomiphene to the regimen may help. One study found that 31% of patients needed this combination, and 67% achieved ovulation within six weeks of starting clomiphene. Regular monitoring, such as tracking menstrual cycles and checking progesterone levels, helps healthcare providers decide when additional treatments might be necessary.
sbb-itb-6dba428
What Affects How Treatment Duration Impacts Results
The timeline for ovulation restoration with metformin depends on several factors. The dosage is one of the most important. Clinical benefits typically don’t show up at doses below 1,000 mg per day, with most women needing between 1,500 and 2,550 mg daily to see optimal results. To ease gastrointestinal discomfort, it’s recommended to start with 500 mg alongside your largest meal and gradually increase to 500 mg three times daily over four to six months.
Body weight and insulin resistance levels also play a major role in how long treatment takes. A study involving 150 obese women with PCOS found that metformin led to about a 10% reduction in BMI, which subsequently improved ovulation rates. However, higher levels of insulin resistance and body weight can extend the time needed for ovulation restoration. Combining metformin with a low-calorie diet can help accelerate weight loss and improve ovulation outcomes. These factors lay the groundwork for understanding how additional therapies can further refine treatment timelines.
In a case series of 48 women, 40% were able to ovulate with metformin alone. For the remaining women, adding clomiphene citrate (50 mg) helped 67% achieve ovulation within six weeks. This combination approach is especially effective when metformin alone isn’t enough. Research from 19 studies involving 1,790 women shows that combining metformin with clomiphene increases clinical pregnancy rates (OR 1.62, 95% CI 1.32–1.99) compared to using clomiphene alone.
Another key factor is adherence to treatment, especially given the side effects. About 40% of patients experience gastrointestinal issues, but only 10% need to lower their dose, and just 2% discontinue treatment entirely. For those who struggle with oral metformin, topical formulations provide a helpful alternative. These versions are easier on the stomach and allow patients to stick with the treatment more consistently. Companies like Oana Health offer topical metformin starting at $89 per month, providing a solution for patients who find oral formulations challenging.
"I'm so glad I discovered Oana's metformin lotion! I used to struggle a lot with the side effects for oral metformin and this is a great alternative for me. I get the same benefits but no more upset stomach and nausea, and this helps me stick with it a lot more consistently." - Carrie S., Topical Metformin user [1]
Medical Guidelines for Using Metformin to Treat PCOS
Start metformin at 500 mg with your largest meal, gradually increasing the dose by 500 mg per meal as tolerated. The usual target dose for managing PCOS falls between 1,500 and 2,550 mg daily, as clinical effects are rarely observed at doses below 1,000 mg per day. This gradual increase helps reduce gastrointestinal side effects while reaching an effective therapeutic level. These dosing strategies reflect common practices in PCOS management.
Ovulation generally begins within 4–6 months of treatment, according to the American Academy of Family Physicians. Research shows that over 90% of women experience regular menstrual cycles after at least six months of therapy. Additionally, studies suggest that metformin-based treatment improves conception rates within the first 4–6 months for women who respond positively to the medication.
Leading health organizations also highlight metformin’s ability to restore ovulation. The NHS explains that metformin helps lower insulin and blood sugar levels, which can promote ovulation, regulate menstrual cycles, and reduce the risk of miscarriage. Cochrane reviews provide moderate-quality evidence suggesting that metformin increases clinical pregnancy rates compared to a placebo, though it may cause more gastrointestinal side effects. If ovulation does not occur after 4–6 months of metformin at a therapeutic dose, adding clomiphene citrate (50 mg) or letrozole is recommended.
For better adherence, extended-release metformin offers the convenience of once-daily dosing and improved gastrointestinal tolerance. Oana Health provides Oral Metformin ER for $22 per month, offering a telehealth-based treatment option with licensed medical professionals, free shipping, and support for long-term therapy aimed at enhancing ovulation and fertility outcomes.
Confirm that you’re not pregnant with a negative home test and maintain two weeks of abstinence before starting metformin. If trying to conceive, it’s recommended to have intercourse every 2–3 days. For those not planning pregnancy, reliable contraception is essential, as metformin can restore fertility. Ongoing monitoring should include blood tests to confirm ovulation, tracking menstrual cycles, and keeping an eye on weight and metabolic markers throughout treatment.
Conclusion: What to Know About Metformin and Ovulation
The effectiveness of metformin in supporting ovulation largely depends on how long the treatment is followed. While some women notice changes within the first few months, research suggests that consistent use over 3–6 months - or even longer - yields the best results. For instance, one study found that 40% of participants resumed spontaneous ovulation, and 69% conceived within six months. When treatment extended beyond six months, over 90% of women reported regular menstrual cycles.
Consistency and proper dosing are key. Daily doses under 1,000 mg often fail to produce results, whereas doses between 1,500–2,550 mg taken consistently over several months are more effective. Gastrointestinal side effects, which affect 21–40% of users, can be managed by taking metformin with meals, gradually increasing the dose, or using extended-release versions for better tolerance.
Incorporating lifestyle changes can also amplify metformin's benefits. For example, reducing BMI by just 10% has been shown to significantly improve ovulation rates. Women who combine metformin with a healthy diet and regular exercise often see better outcomes compared to those relying on medication alone. If ovulation hasn’t occurred after 4–6 months at an effective dose, combining metformin with medications like clomiphene or letrozole may improve success rates. Research shows that combination therapy increases clinical pregnancy rates, with an odds ratio of approximately 1.62 compared to using clomiphene alone. Adding telehealth support to this approach can further enhance results by making treatment more accessible and easier to maintain.
Telehealth platforms, such as Oana Health, offer personalized options like Oral Metformin ER starting at $22 per month. These services include automatic refills, free shipping, and continuous support, helping women maintain the consistent, long-term treatment required to optimize ovulation and fertility outcomes.
Regularly tracking menstrual cycles and staying in touch with healthcare providers is essential for adjusting treatment as needed. With the right dose, duration, and support system, metformin has proven to be an effective tool for restoring ovulation in many women with PCOS, as evidenced by the research and guidelines discussed throughout this article.
FAQs
How does metformin support ovulation in women with PCOS?
Metformin helps women with PCOS ovulate by enhancing the body’s response to insulin. This improvement lowers insulin levels, which can help correct the hormonal imbalances that often interfere with ovulation.
By targeting insulin resistance, metformin encourages a steadier hormonal cycle, making ovulation more consistent over time. For many women with PCOS, this can be an effective part of a broader treatment strategy designed to meet their specific needs.
What can I do if metformin causes stomach upset or nausea?
If metformin is giving you stomach troubles or making you feel nauseous, you could explore a topical form of metformin. This option might be easier on your digestive system. Another approach is to discuss with your healthcare provider about tweaking your dosage or looking into alternative ways to manage the side effects. They can guide you toward a plan that balances your comfort with the treatment's effectiveness.
When should I consider combining clomiphene with metformin to improve ovulation?
If you’ve been using metformin for a steady 3 to 6 months and haven’t noticed improvements in ovulation or it’s still irregular, it might be worth discussing the addition of clomiphene with your doctor. This combination is often beneficial for women with PCOS who don’t experience regular ovulation while on metformin alone.
Be sure to consult your healthcare provider to explore the best treatment options tailored to your needs and goals.
