Microbiome Modulation for Androgen Excess
Androgen excess, often linked to conditions like PCOS, affects millions of women and can lead to symptoms such as unwanted hair growth, acne, weight gain, and irregular cycles. Emerging research highlights a connection between gut health and hormone regulation, showing that an imbalanced microbiome can worsen androgen levels, insulin resistance, and inflammation.
Here’s what you need to know:
- Gut diversity matters: Women with PCOS often have less diverse gut bacteria, which can disrupt hormone balance.
- Diet plays a role: High-fiber foods and probiotics can support gut health and lower androgen production.
- Lifestyle changes help: Exercise, stress management, and sleep improve microbiome health and hormone regulation.
- Targeted treatments: Combining medications like Metformin and Spironolactone with gut-focused strategies can address both symptoms and root causes.
The Gut–PCOS Connection: Inflammation, Insulin Resistance, and Solutions | Felice Gersh, MD
The Gut Microbiome and Hormone Regulation
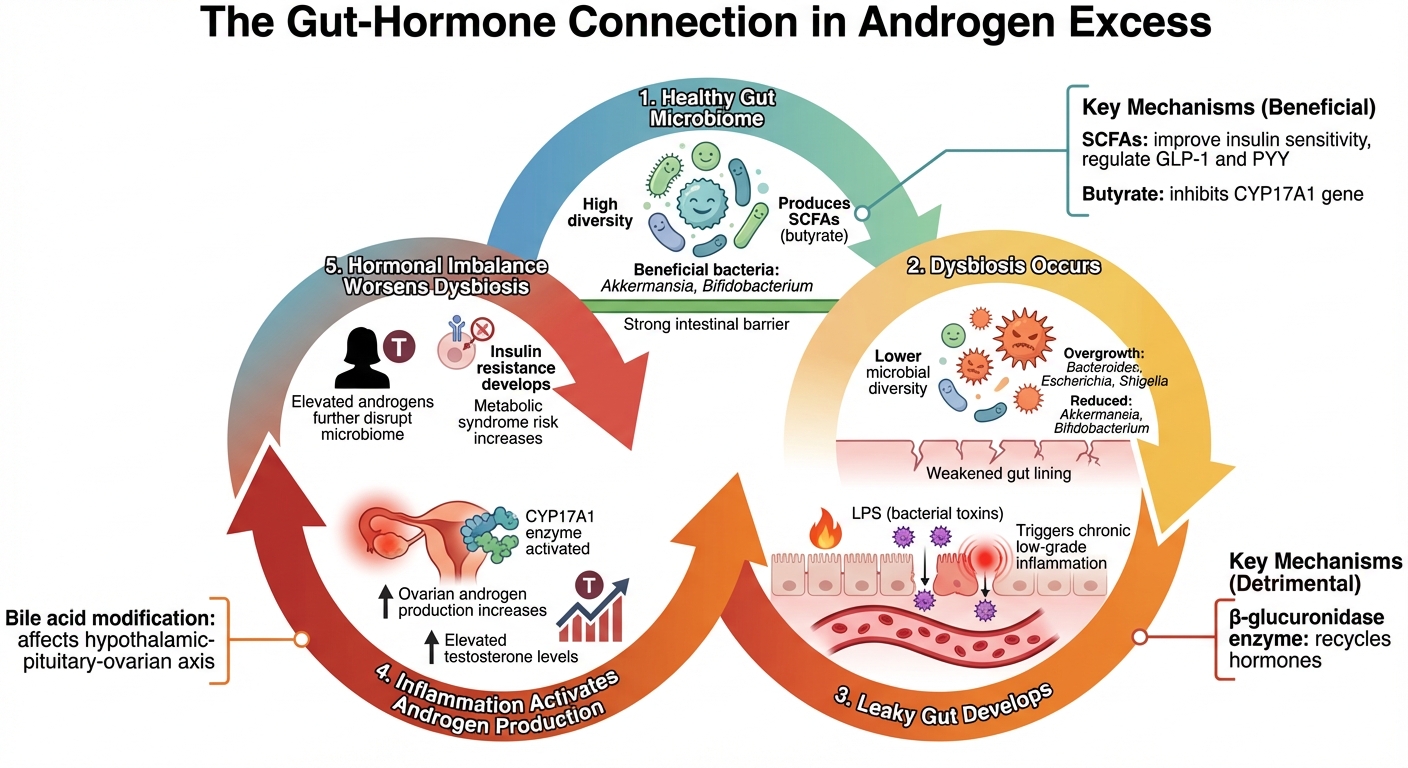
How Gut Microbiome Affects Androgen Levels: The Dysbiosis-Hormone Cycle
What Is the Gut Microbiome?
The gut microbiome is a vast and intricate community of bacteria living in your digestive system. These trillions of microorganisms carry immense genetic diversity and play a role in countless bodily processes. Because of its extensive influence, some scientists even refer to it as a "separate organ" or an "endocrine organ", emphasizing its role in regulating hormones.
How the Microbiome Affects Hormones
Gut bacteria have several ways of interacting with and influencing hormones. For instance, they produce an enzyme called β-glucuronidase, which helps recycle hormones by breaking them down so they can be reabsorbed. They also ferment dietary fiber into short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which improve insulin sensitivity and regulate gut peptides like GLP-1 and PYY. Additionally, gut microbes modify bile acids, which then interact with receptors that affect key hormonal pathways, including the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis and androgen production. These complex interactions reveal how the gut microbiome plays a central role in maintaining hormonal balance - or, when disrupted, contributing to imbalances.
Dysbiosis and Elevated Androgen Levels
When the gut microbiome becomes unbalanced - a condition known as dysbiosis - it can significantly disrupt hormone regulation, especially in women. Dysbiosis is closely linked to elevated androgen levels, a hallmark of conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Research shows that women with PCOS often have lower microbial diversity in their gut compared to those without the condition. Their gut bacteria tend to include an overgrowth of Gram-negative species such as Bacteroides, Escherichia, and Shigella, while beneficial bacteria like Akkermansia and Bifidobacterium are reduced.
This imbalance can lead to a "leaky gut", where the intestinal lining becomes more permeable. As a result, bacterial toxins like lipopolysaccharides (LPS) can enter the bloodstream. These toxins trigger chronic, low-grade inflammation, which in turn activates the enzyme CYP17A1. This enzyme plays a key role in increasing ovarian androgen production. A study published in the Journal of Translational Medicine highlights this connection:
"The gut microbiota of PCOS patients may be associated with the development and occurrence of hyperandrogenism, insulin resistance, chronic inflammation, and metabolic syndrome."
This creates a harmful cycle: elevated androgen levels further disrupt the gut microbiome, worsening hormonal imbalances and metabolic issues. Such findings underscore the potential of gut-focused therapies to help manage androgen excess and improve overall health.
How to Improve Gut Health to Reduce Androgen Excess
Dietary Changes for a Healthier Microbiome
What you eat plays a huge role in shaping your gut bacteria and hormone levels. High-fiber foods, for example, feed the good bacteria in your gut. These bacteria produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which help strengthen your intestinal lining and prevent "leaky gut." Why does this matter? When your gut barrier is weak, inflammatory toxins can escape into your bloodstream, triggering excess androgen production.
The Mediterranean diet is a great option for promoting a healthy gut microbiome. It focuses on plant-based fats, lean proteins, and high-fiber vegetables, which help manage hormonal imbalances often seen in conditions like PCOS. On the flip side, diets loaded with unhealthy fats and calories can disrupt your gut's balance, increasing the ratio of Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes bacteria - a pattern closely tied to obesity-related hormone issues.
Adding at least 10 grams of inulin to your daily diet can also make a difference. Inulin supports gut bacteria that improve insulin sensitivity and lower androgen levels. Clinical studies have shown that taking probiotics for 12 weeks can raise sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) by an average of 3.95 nmol/ml, which helps reduce free androgen levels. Foods like wheat bran are another great choice - they provide a foundation for lactic acid bacteria to create protective layers in your gut. Keeping your glycemic load in check is just as important since lower insulin levels mean your ovaries are less likely to produce excess androgens.
These dietary shifts set the stage for using probiotics and prebiotics to fine-tune your gut and hormone balance.
Using Probiotics and Prebiotics
Once you've made dietary changes, supplements like probiotics and prebiotics can take things a step further. Together, they help restore gut balance and regulate hormones. Prebiotics ferment in your gut to produce SCFAs, which block harmful bacterial toxins (like lipopolysaccharides or LPS) from entering your bloodstream. This prevents inflammation that can lead to increased androgen production.
One key SCFA is butyrate, which acts as a natural inhibitor of the CYP17A1 gene - a gene that drives excessive androgen production. Without enough butyrate, this gene can become overactive. Probiotics also play a role in regulating bile acids, converting them into forms like deoxycholic acid. This activates the Farnesoid X receptor (FXR), which boosts liver enzymes (like SULT2A1 and CYP3A4) that help clear androgens from your system.
When choosing a probiotic, look for strains like Lactiplantibacillus plantarum or Bifidobacterium lactis V9. These strains have been shown to help balance testosterone and luteinizing hormone (LH) levels. Prebiotic supplements, such as Arabic gum (Acacia senegal), may also help lower LH and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) levels. These supplements improve insulin sensitivity by stimulating glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), reducing the insulin spikes that can drive your ovaries to overproduce androgens.
Lifestyle Factors That Support Gut Health
Lifestyle choices are just as important as diet and supplements when it comes to gut health and hormone balance. Regular exercise, for instance, can reshape your gut microbiome in a positive way. It encourages the growth of beneficial bacteria like Faecalibacterium, Roseburia, and Akkermansia muciniphila, while reducing harmful Proteobacteria. High-intensity workouts, in particular, improve insulin sensitivity. In fact, studies show that daily exercise can improve menstrual irregularities and ovulation in half of women with PCOS.
Exercise also activates the bile acid-FXR pathway, which enhances liver clearance of androgens. Plus, it promotes the growth of butyrate-producing bacteria, which helps suppress the CYP17A1 gene - a key player in androgen excess.
Managing stress is equally important. Chronic stress can weaken your gut lining, allowing toxins like LPS to enter your bloodstream and spark ovarian inflammation. This inflammation directly activates enzymes that ramp up androgen production. Practices like yoga can help. Studies show that doing yoga for at least three months can significantly lower testosterone and LH levels. Sleep quality is another critical factor. Poor sleep disrupts your gut microbiome and affects the BMAL1 gene, which is linked to insulin resistance, hyperandrogenism, and irregular ovulation. Sticking to a consistent sleep schedule helps protect this gene and supports melatonin production, which is essential for follicle development and hormone regulation.
sbb-itb-6dba428
Personalized Treatment Options for Androgen Excess
How Telehealth Helps with Hormonal Imbalances
Managing androgen excess calls for tailored care. Studies indicate that between 80% and 90% of women with elevated androgen levels have PCOS, yet around 70% of women with PCOS remain undiagnosed worldwide. Telehealth bridges the gap by connecting patients with specialists who understand the intricate relationship between hormones and gut health.
Through virtual visits, telehealth enables metabolic monitoring and the creation of integrated treatment plans. These plans blend traditional medications with strategies targeting the microbiome. Instead of solely relying on symptom management with birth control pills, licensed medical professionals craft approaches that address immediate issues like acne or unwanted hair growth, while also tackling root causes such as insulin resistance and gut imbalances.
Prescriptions are conveniently delivered to your doorstep, making it easier to stick to your treatment. This comprehensive, patient-focused approach is a hallmark of Oana Health’s science-driven protocols.
Oana Health's Treatment Approach
Oana Health combines prescription medications with strategies designed to support microbiome health. Their licensed professionals prescribe treatments like Spironolactone (starting at $14/month), which reduces androgen effects on hair follicles and skin, and Metformin (starting at $22/month), which enhances insulin sensitivity and helps balance gut microbiota. Research has shown that pairing probiotics with Metformin can significantly improve blood sugar control compared to using Metformin alone.
For additional support, Oana Health offers GLP-1 medications (starting at $199/month). These treatments help regulate appetite and glucose metabolism, processes that are naturally influenced by short-chain fatty acids produced by gut bacteria. For women whose androgen levels are linked to weight issues, weight loss treatments can also improve gut health by reducing excess body fat.
To address unwanted facial hair, options like Eflornithine or Hairless Hype ($69/month) are available. Hair loss can be managed with Oral Minoxidil ($25/month) or Topical Spironolactone ($43/month). All treatments include free shipping and are prescribed after a detailed review of your health history. This ensures your plan is customized to your specific needs, whether you have lean or obese PCOS phenotypes, which often arise from different underlying factors.
Conclusion
Your gut microbiome plays a crucial role in regulating androgen levels, with low microbial diversity often linked to inflammation, insulin resistance, and excessive testosterone production. By focusing on gut health - through dietary fiber, probiotics, and regular exercise - you can address the root causes of hormonal imbalances instead of merely managing the symptoms.
Healthy gut bacteria produce short-chain fatty acids, like butyrate, which help inhibit enzymes responsible for androgen production and strengthen the intestinal barrier. When this barrier is weakened, harmful bacterial toxins can enter the bloodstream, triggering excess androgen production. Maintaining a balanced microbiome not only helps restore hormonal harmony but also lays the groundwork for more tailored treatment options.
Personalized care is key. Conditions like PCOS and androgen excess affect every woman differently. Platforms such as Oana Health offer a combination of prescription medications and microbiome-focused strategies designed to meet your specific needs. This integrated approach tackles both immediate symptoms and the underlying gut-hormone connection.
Effectively managing androgen excess requires a comprehensive approach. Dietary and lifestyle changes serve as the foundation, while prescription treatments like Metformin and Spironolactone complement a healthy gut microbiota to achieve hormonal balance. With the right personalized plan, you can work toward long-term hormonal stability and better overall health.
FAQs
How does the gut microbiome impact androgen levels in women with PCOS?
The gut microbiome plays a crucial role in managing androgen levels in women with PCOS. When the balance of gut bacteria is disrupted - such as changes in the Bacteroidetes/Firmicutes ratio or an overgrowth of bacteria like Escherichia or Shigella - it can lead to systemic inflammation and interfere with hormone regulation. This disruption may result in the production of certain metabolites that affect steroid hormone synthesis, which can worsen symptoms linked to androgen excess.
Focusing on gut health through specific interventions could help reduce inflammation, rebalance the microbiome, and alleviate PCOS-related symptoms, including acne, hair thinning, and excessive facial hair growth.
What foods can support gut health and help manage androgen excess?
Improving gut health through your diet can make a big difference in managing androgen excess, especially for women dealing with PCOS. Start by including plenty of fiber-rich, prebiotic foods in your meals - think oats, barley, legumes, apples, onions, garlic, and chicory. These foods feed the good bacteria in your gut, which play a role in regulating insulin levels and reducing ovarian androgen production. Adding fermented foods like plain yogurt, kefir, kimchi, or sauerkraut can also boost microbial diversity and help reduce inflammation linked to hormonal imbalances.
On the flip side, it’s important to cut back on high-glycemic carbs and added sugars - such as white bread, pastries, and sugary drinks - since they can worsen insulin resistance. Instead, opt for whole-grain alternatives like brown rice, quinoa, or whole-wheat pasta. Pair these with healthy fats from sources like olive oil, avocados, nuts, and fatty fish. To round out your meals, include moderate protein from plant-based options like lentils, beans, or tofu, along with occasional lean animal protein to maintain balance without compromising gut health.
By focusing on a diet packed with fiber, probiotics, and healthy fats while cutting down on refined carbs and sugars, you can support your gut microbiome and hormonal balance naturally - helping to ease androgen-related symptoms.
How can probiotics and prebiotics help with hormonal imbalances caused by androgen excess?
Probiotics, which are live bacteria that benefit your health, and prebiotics, the fibers that nourish them, play a vital role in maintaining a balanced gut microbiome. For women dealing with androgen excess, an imbalanced gut can fuel inflammation and insulin resistance - two factors that can trigger higher androgen production. By improving gut health, probiotics and prebiotics can help address these underlying issues and promote better hormonal balance.
Certain probiotic strains also produce metabolites that interact with the body's hormone-regulating systems. These interactions can help stabilize testosterone and estrogen levels. Research has shown that using these supplements can alleviate symptoms such as acne, excess hair growth, and irregular menstrual cycles. They may also enhance ovulation and contribute to overall hormonal well-being.
To address androgen-related concerns with precision, Oana Health’s licensed clinicians offer personalized probiotic and prebiotic recommendations as part of a broader care plan.
