Topical Minoxidil Side Effects: Systemic Absorption Risks
Topical minoxidil, widely used for hair regrowth, can sometimes lead to systemic absorption, causing side effects beyond the scalp. Though only about 1.4% of the medication typically enters the bloodstream, factors like damaged skin, excessive doses, or improper application can increase this rate and lead to symptoms such as rapid heartbeat, fluid retention, or dizziness. To minimize risks:
- Stick to recommended doses: 1 mL twice daily.
- Apply only to healthy, dry skin.
- Avoid occlusion: Let the product dry before covering the scalp.
- Watch for warning signs: Chest pain, swelling, or sudden weight gain require immediate medical attention.
If you experience side effects or see no improvement after 4–6 months, consult a doctor about alternatives like oral minoxidil or topical spironolactone.
Minoxidil Side Effects - Is the Hair Regrowth Worth It? A Doctor Weighs In
Signs of Systemic Absorption
When minoxidil is absorbed systemically, its effects extend beyond the scalp, potentially impacting the cardiovascular system, the nervous system, and fluid regulation. These symptoms act as warning signs of heightened absorption and demand swift medical attention.
Physical Symptoms
Unusual hair growth (hypertrichosis) on areas like the face, hands, or body can signal systemic absorption. Another red flag is sudden, unexplained weight gain accompanied by swelling in the face, hands, feet, or lower legs - this points to fluid retention. Other physical signs include skin flushing, numbness, tingling sensations, or blurred vision.
While these visible changes are concerning, systemic absorption can also have serious effects on the heart and nervous system.
Heart and Nervous System Symptoms
"Minoxidil overdose can cause a broad range of serious cardiovascular side effects, including severe circulatory shock due to its direct vasodilatory effect, fluid retention, pulmonary edema, tachycardia-induced acute heart failure, and subendocardial ischemia."
– Sabin Tripathee, MD, Internal Medicine Resident, Jefferson Einstein Montgomery Hospital
New or worsening chest pain is a critical warning sign that requires immediate attention. A rapid, pounding, or irregular heartbeat (tachycardia) may indicate that minoxidil is affecting your cardiovascular system. In severe cases, heart rates can exceed 150 beats per minute.
Given minoxidil’s vasodilatory action, neurological symptoms like dizziness, lightheadedness, or fainting sensations should not be ignored. Other concerning signs include headaches, confusion, extreme fatigue, and shortness of breath - particularly when lying down. If you notice any of these issues, it’s essential to stop using minoxidil immediately and consult a healthcare provider.
What Increases Absorption Risk
Several factors can lead to increased systemic absorption of minoxidil, often due to application errors or external conditions. These issues not only reduce the effectiveness of the treatment but also raise the likelihood of side effects.
Application Mistakes
Using more than the recommended dose of 1 mL per application - roughly six sprays or half a capful - can significantly increase the risk of systemic absorption. This is especially true when higher concentrations, like the 5% solution, are used. For instance, clinical trials have shown that approximately 4% of women using the 5% solution experienced unwanted facial hair growth, a side effect less common with the 2% version.
Applying minoxidil to damaged skin is another critical mistake. Damaged skin, such as areas that are red, swollen, or broken, lacks the protective barrier necessary to regulate absorption, allowing higher amounts of the drug to enter the bloodstream.
"Any other skin problems, an irritation, or a sunburn on the scalp - These conditions may cause too much topical minoxidil to be absorbed into the body and may increase the chance of side effects."
– Mayo Clinic
Additionally, poor hygiene practices, like failing to wash hands after application or mixing minoxidil with other skin products, can lead to unintended absorption in sensitive areas.
Environmental and Lifestyle Factors
External factors can also play a significant role in increasing absorption. For example, covering the scalp too soon after applying minoxidil creates occlusion, which drives the medication deeper into the skin. A case reported in the American Journal of Case Reports highlighted how prolonged scalp occlusion led to extensive systemic absorption.
"The patient's scalp was constantly occluded, day and night. This resulted in much greater penetration of minoxidil into the scalp than with regular application, leading to systemic absorption."
– Vivien Moris, Department of Maxillofacial, Reconstructive, and Aesthetic Plastic Surgery, University Hospital of Dijon
To avoid this, it’s crucial to let the medication dry for 2 to 4 hours before wearing hats, wigs, or going to bed. Within the first hour, about 50% of minoxidil is absorbed, and this increases to 75% after four hours. If you go to bed too soon, the wet medication can transfer to your pillowcase, potentially leading to unintended absorption through contact with other parts of your body.
sbb-itb-6dba428
How to Reduce Absorption Risk
Minimizing the risk of systemic absorption requires careful attention to dosage, application methods, and awareness of warning signs. By following these practical steps, you can ensure safer use of the treatment.
Use the Correct Dose
Stick to the recommended dose: 1 mL (or half a capful of foam) applied twice daily. Using more than this won't improve hair growth and can increase the risk of systemic absorption.
"It is very important that you use this medicine only as directed. Do not use more of it and do not use it more often than your doctor ordered. To do so may increase the chance of it being absorbed through the skin."
– Mayo Clinic
If you forget a dose, apply it as soon as you remember - unless it's almost time for the next one. Never double up on doses to compensate for a missed application.
Apply Only to Healthy Skin
Before each application, examine your scalp for any signs of redness, swelling, sores, or peeling. If you spot any of these, pause the use of minoxidil until your skin has completely healed. Damaged skin can increase the amount of medication absorbed into your bloodstream.
Avoid using other hair treatments that may irritate your scalp until it has fully recovered. If the liquid formulation causes irritation - often due to the presence of propylene glycol - you might want to switch to the foam version, which typically lacks this ingredient.
Ensure your hair and scalp are fully dry before applying the treatment. Resist the urge to use a hairdryer to speed up drying, as heat can reduce the medication's effectiveness.
Watch for Early Warning Signs
Be alert for symptoms of excessive absorption, such as rapid, unexplained weight gain. Other potential warning signs include swelling in the face, hands, feet, or stomach, as well as cardiovascular issues like chest pain, irregular or rapid heartbeat, dizziness, or difficulty breathing.
If you notice any of these symptoms, stop using minoxidil immediately and contact your healthcare provider.
When to Stop and What Alternatives Exist
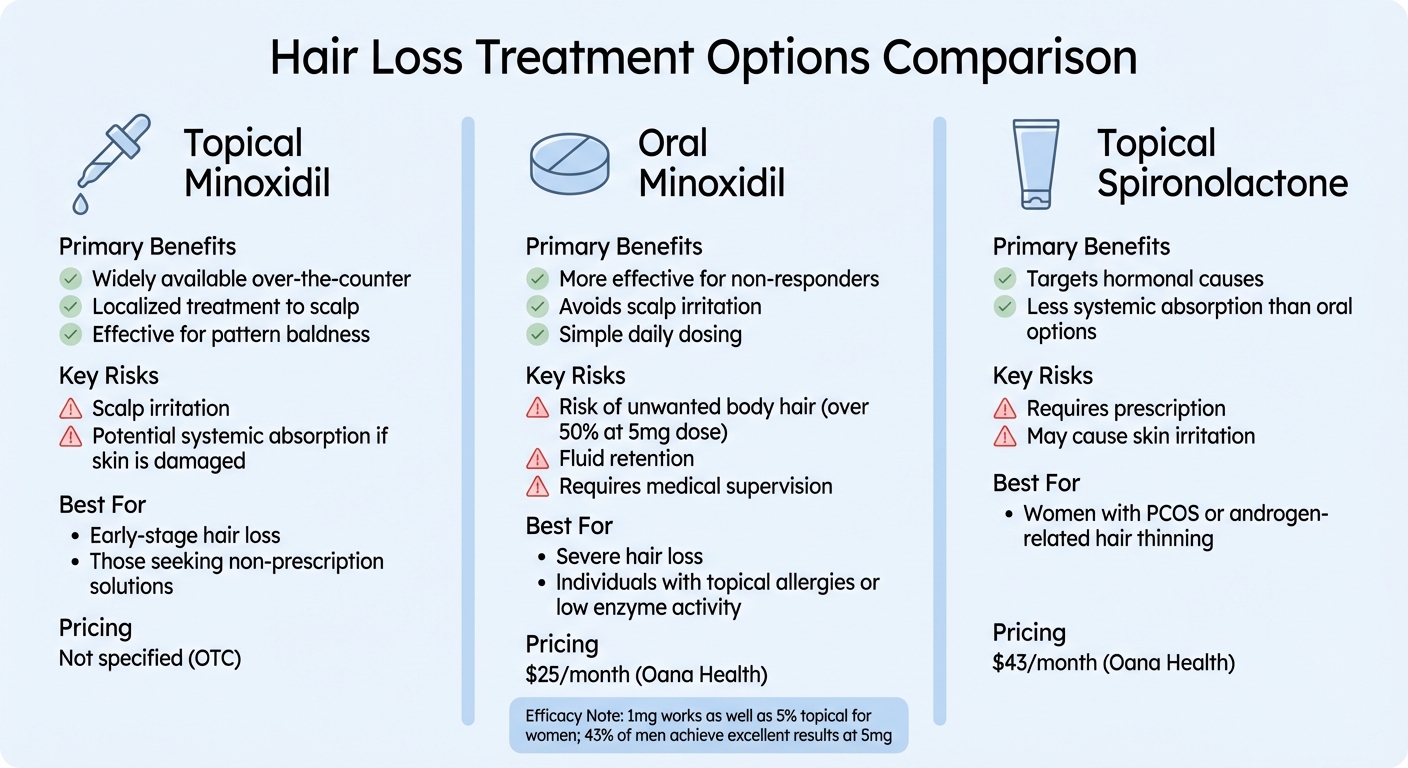
Topical vs Oral Minoxidil vs Topical Spironolactone Treatment Comparison
When to See a Doctor
Stop using topical minoxidil immediately and consult a doctor if you experience any alarming symptoms such as chest pain, rapid or irregular heartbeat, dizziness, fainting, severe allergic reactions (like hives or swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat), unexplained rapid weight gain, or swelling in areas like the hands, feet, ankles, or stomach. Additionally, discontinue use if you notice persistent redness or burning on the scalp, signs of infection (such as yellow, green, or gray discharge), or unwanted hair growth outside the intended treatment area. If you've been using the product consistently for 4 to 6 months without seeing any hair regrowth, it’s time to consult your doctor about other treatment options. Exploring alternatives becomes particularly important if these concerns persist or if the product proves ineffective.
Other Hair Loss Treatments
If topical minoxidil isn’t working for you or causes side effects you can’t tolerate, there are other options that may provide better results while addressing different risks.
Oral minoxidil (available for $25/month through Oana Health) offers a systemic approach to delivering the medication, making it a good option for individuals who don’t respond well to topical application. This treatment is especially effective for those with lower levels of follicular sulfotransferase, the enzyme that activates minoxidil. Plus, oral minoxidil eliminates the hassle of twice-daily scalp applications and avoids the irritation that can come with the topical version.
"Oral minoxidil... may be particularly helpful for patients who are unable to tolerate topical minoxidil or other systemic treatments." – Hassiel Aurelio Ramírez-Marín, Department of Dermatology, Weill Cornell Medical College
Topical spironolactone (priced at $43/month through Oana Health) is another option, particularly for women dealing with hormonal hair loss or conditions like PCOS. By blocking the hormones responsible for hair thinning, this treatment is effective without the higher risk of systemic absorption seen with oral hormone therapies. Since it’s applied directly to the scalp, it’s a more targeted approach.
Treatment Comparison
Here’s a closer look at how these treatment options stack up against each other:
| Treatment | Primary Benefits | Key Risks | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Topical Minoxidil | Widely available OTC; localized treatment; effective for pattern baldness | Scalp irritation; potential systemic absorption if skin is damaged | Early-stage hair loss; those seeking non-prescription solutions |
| Oral Minoxidil | More effective for non-responders; avoids scalp irritation; simple daily dosing | Risk of unwanted body hair (over 50% at 5mg dose); fluid retention; requires medical supervision | Severe hair loss; individuals with topical allergies or low enzyme activity |
| Topical Spironolactone | Targets hormonal causes; less systemic absorption than oral options | Requires a prescription; may cause skin irritation | Women with PCOS or androgen-related hair thinning |
Research shows that low-dose oral minoxidil (1mg) can work as well as a 5% topical minoxidil solution for women with pattern hair loss, with fewer than 2% discontinuing due to side effects. For men taking 5mg of oral minoxidil, 43% achieved excellent hair growth results.
Conclusion
Topical minoxidil can be an effective solution when used properly. To get the best results, apply the recommended dose to dry, healthy skin. This helps reduce the risk of the medication being absorbed into your bloodstream, which can lead to unwanted side effects.
Pay close attention to how your body reacts, especially during the first few weeks. Experiencing mild irritation or some initial shedding is common, but if you notice symptoms like chest pain, a rapid heartbeat, dizziness, or sudden weight gain, seek medical attention immediately.
"Monitoring your body's response closely during the first few weeks of use can help prevent serious complications." – Dr. Kalyani Deshmukh, MD (Dermatology, Venerology, and Leprosy)
For most people, proper application and regular monitoring are enough to see positive results. However, if you don’t notice any improvement after 4 to 6 months or if side effects persist, it’s time to stop treatment and consult a specialist. Oana Health provides personalized, prescription-based alternatives that can be conveniently delivered to your door with free shipping.
Consulting a dermatologist or trichologist is essential for a correct diagnosis and a treatment plan tailored to your type of hair loss. This is especially important if you have pre-existing heart conditions, are pregnant or breastfeeding, or are taking medications that could interact with minoxidil. Working with a professional ensures your treatment is safe and effective.
FAQs
What are the symptoms of systemic absorption from topical minoxidil?
Systemic absorption of topical minoxidil can sometimes result in noticeable side effects like a rapid heartbeat (tachycardia), dizziness, or swelling in the hands or feet. These symptoms suggest the medication might be impacting areas of the body beyond the scalp.
To minimize this risk, stick to the recommended dosage and avoid using the product on broken or irritated skin. If you notice any unusual symptoms, reach out to a healthcare provider right away for advice.
What can I do to minimize the risk of side effects from systemic absorption when using topical minoxidil?
To minimize the chance of the body absorbing too much minoxidil, stick to the recommended amount and apply it only to a clean, dry scalp. Avoid using it on broken skin or anywhere other than the scalp. After applying, wash your hands thoroughly to prevent it from spreading to other areas of your body. If you're concerned about side effects, consider using a lower-strength formula or ask your healthcare provider about alternatives, such as a low-dose oral option. Always follow your doctor's guidance for safe and effective use.
What should I do if I experience side effects while using topical minoxidil?
If you notice side effects like itching, redness, burning, or increased hair shedding, stop using minoxidil right away. Gently clean the affected area with mild soap and water to soothe irritation. However, if you experience more severe symptoms - such as dizziness, swelling, or trouble breathing - discontinue use immediately and reach out to your healthcare provider.
For your well-being, it’s always a good idea to consult a licensed medical professional if you’re unsure about your reaction or need advice on what to do next. Acting quickly can help address side effects and keep your treatment plan moving forward.
