Topical vs. Oral Androgen Blockers: What to Know
Looking to manage hair loss, acne, or hormonal imbalances? You might be considering androgen blockers. These treatments come in two forms: topical (creams, gels) and oral (pills).
Here’s the quick breakdown:
- Topical blockers work locally, targeting specific areas like the scalp or skin. They have fewer side effects since they don’t enter the bloodstream as much. However, they require daily application and are less effective for widespread hormonal issues.
- Oral blockers affect the entire body, making them effective for multiple symptoms like acne, unwanted hair, and hormonal imbalances. But they carry systemic risks like liver issues or birth defect risks and often need regular blood tests.
Quick Comparison
| Feature | Topical Blockers | Oral Blockers |
|---|---|---|
| Application | Applied to specific areas (e.g., scalp, face) | Taken as a pill, once daily |
| Effectiveness | Localized impact (e.g., hair loss, acne) | Systemic impact for multiple symptoms |
| Side Effects | Mild skin irritation (7–17%) | Systemic risks (e.g., liver, potassium issues) |
| Convenience | Requires daily application | Easier to incorporate into routines |
| Cost | Starts around $43/month | Starts around $14/month |
Both options take 3–6 months to show results. Your choice depends on the severity of symptoms, your tolerance for side effects, and lifestyle preferences. Always consult a doctor before starting treatment, especially if you’re pregnant or planning to conceive.
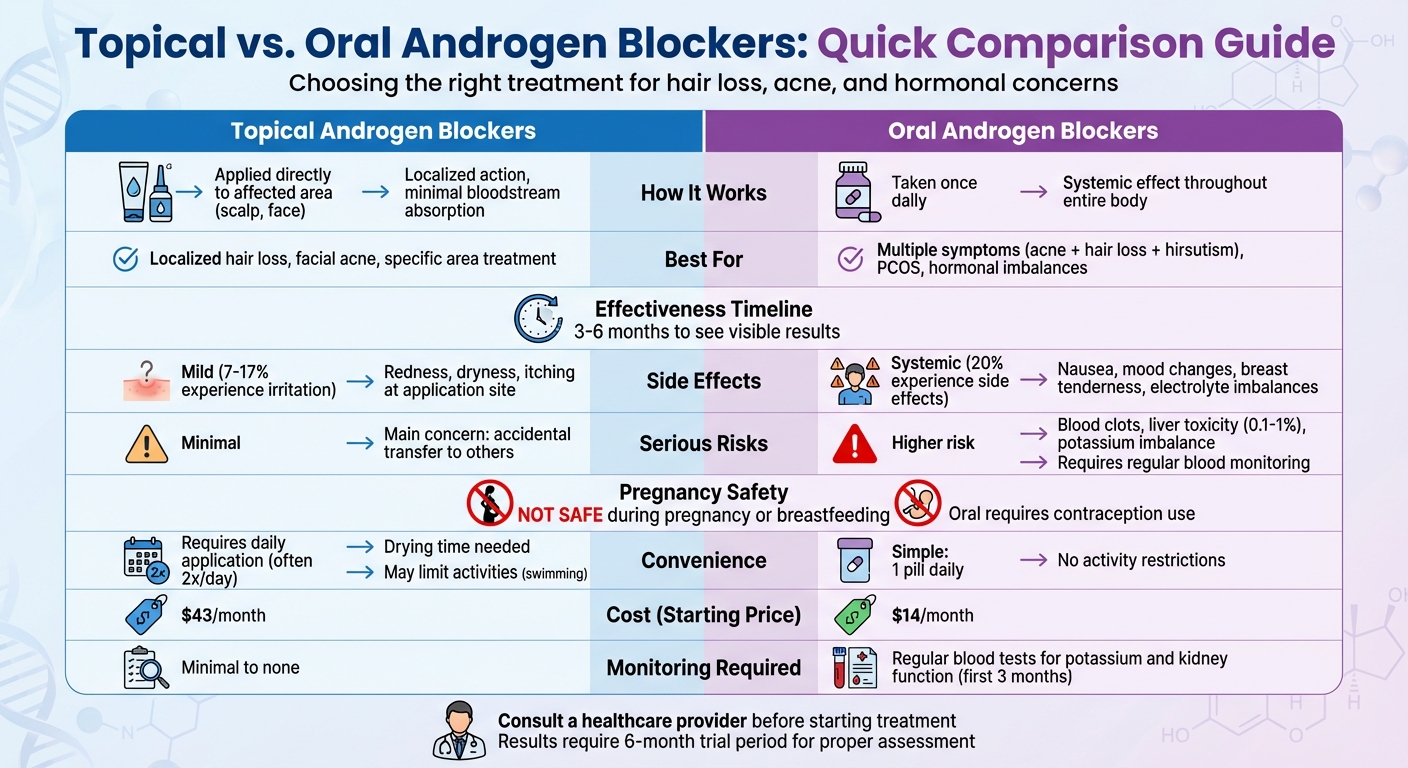
Topical vs Oral Androgen Blockers Comparison Chart
Topical Finasteride: Same Results, No Side Effects?
How Topical Androgen Blockers Work
Topical androgen blockers are designed to be applied directly to the skin - whether it's the scalp, face, or another affected area. Once applied, they target androgen receptors located in the sebaceous glands and at the base of hair follicles, helping to address various skin and hair conditions. These treatments work in one of two main ways: either by blocking androgen receptors to prevent testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT) from attaching or by inhibiting the enzyme 5-alpha reductase, which converts testosterone into the more potent DHT within the skin. The unique advantage of topical treatments lies in their ability to concentrate the medication in the dermis, allowing for localized effects while minimizing absorption into the rest of the body.
This localized action sets topical treatments apart from oral medications. Unlike oral drugs that impact hormone levels throughout the entire body, topical blockers act only where applied. For example, in acne treatment, they reduce sebum production and help prevent clogged pores in the treated area. Similarly, for hair loss, they target DHT activity in the scalp without significantly altering hormone levels elsewhere in the body. This approach leads to far fewer systemic side effects compared to oral medications. While oral treatments can cause side effects like menstrual irregularities or electrolyte imbalances, topical options keep the medication concentrated at the application site, reducing such risks.
This targeted delivery system is what makes topical treatments stand out.
Benefits of Topical Androgen Blockers
One of the biggest advantages of topical androgen blockers is their minimal systemic absorption. Because the medication stays primarily in the skin, many of the body-wide side effects seen with oral treatments are avoided. Another key benefit is the precision of treatment. For instance, clascoterone cream 1% (Winlevi), which is FDA-approved for acne, is applied only to the affected areas twice daily. Clinical trials for topical formulations like finasteride and cortexolone 17α‑propionate (C17P) for hair loss have shown minimal side effects. Topical finasteride, for example, has been found to reduce scalp DHT levels by up to 70%, compared to 50% with its oral counterpart.
For individuals who can’t take oral medications due to contraindications or side effects, topical treatments offer a practical alternative. They can also be combined with other therapies, such as topical minoxidil, to improve hair regrowth results.
Still, as effective as they are, topical treatments do come with their own set of challenges.
Drawbacks of Topical Androgen Blockers
One of the main downsides of topical treatments is the commitment to daily application. Unlike swallowing a pill, these treatments often require once or twice-daily application to the affected area. Results also take time, with at least a six-month trial period recommended before assessing effectiveness or making changes to the treatment plan. Additionally, some users experience local side effects, such as irritation, redness, or itching. For instance, 7% of patients report irritation at the application site, while 5% experience redness.
Another limitation is that topical blockers are inherently localized in their effects. They are ideal for treating specific areas but may not be effective for broader hormonal issues or conditions like severe hirsutism or polycystic ovary syndrome, which often require systemic treatment. There’s also the risk of secondary exposure - if the treated area isn’t properly covered or hands aren’t washed after application, others, particularly women or children, might experience unintended effects like acne or hair growth.
Lastly, some promising topical formulations are still awaiting FDA approval in the United States. For example, while topical finasteride is approved for use in countries like Italy, Germany, and South Korea, it remains unlicensed for hair loss treatment in the U.S. as of 2025. These regulatory hurdles highlight the ongoing need for safety evaluations and clinical studies.
How Oral Androgen Blockers Work
Oral androgen blockers work throughout the body by entering the bloodstream and targeting hormones at their source. Unlike topical treatments, which act locally, oral medications impact the entire hormonal system. They achieve this by either reducing hormone production from the pituitary gland, ovaries, or adrenal glands, or by blocking androgen receptors in various tissues.
One commonly prescribed oral blocker, spironolactone, works by competing with androgens for receptor binding in different tissues. Oral contraceptives, on the other hand, take a different approach. They stimulate the liver to produce more Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin (SHBG), a protein that binds free testosterone in the bloodstream. This process reduces free testosterone levels by about 50%, effectively neutralizing its activity.
This systemic approach provides broad benefits but also comes with potential risks.
Benefits of Oral Androgen Blockers
Oral androgen blockers are particularly effective for women dealing with hormonal imbalances, such as those caused by PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome). These medications can help restore hormone balance, regulate menstrual cycles, and lower the risk of endometrial hyperplasia or cancer. PCOS is a common condition, affecting 5% to 10% of women and standing as the leading cause of infertility in the United States.
"Polycystic ovary syndrome is the most common cause of infertility in the United States." - Merck Manual
Oral treatments can tackle multiple androgen-related symptoms at once. For example, if you're facing acne, unwanted facial hair, and hair loss, a single oral medication might address all three issues. When using oral contraceptives with anti-androgenic properties, acne often improves by 40% to 50% within three cycles and by 80% to 90% after nine cycles. Similarly, cyproterone acetate has been shown to reduce unwanted body hair in 50% to 75% of women.
One of the biggest advantages of oral pills is their convenience. A single daily dose can address multiple symptoms without requiring localized application or concerns about secondary exposure.
Drawbacks of Oral Androgen Blockers
The systemic nature of oral androgen blockers, while effective, can lead to side effects like hot flashes, decreased libido, fatigue, and muscle loss. Spironolactone, though generally well-tolerated, can cause electrolyte imbalances, particularly high potassium levels, which may affect heart rhythm. Regular monitoring of potassium and creatinine levels is especially important for older women or those with kidney or heart conditions.
"The teratogenic potential of these drugs means that they should be used in conjunction with adequate contraception in women of reproductive age." - Mohamed Yahya Abdel-Rahman, MD, Medscape
Pregnancy precautions are essential. Medications like spironolactone and finasteride carry a significant risk of birth defects in male fetuses. Women of childbearing age must use effective contraception while taking these drugs, which can make treatment more complicated.
Some oral blockers also pose serious safety risks. For instance, while flutamide is often more effective than spironolactone for treating hirsutism, it is not FDA-approved for this use due to its potential to cause fatal liver damage. Close monitoring for liver health is required when using this medication. Additionally, long-term use of GnRH agonists beyond six months necessitates "add-back" therapy with estrogen or hormone replacement to prevent severe bone density loss.
Cost is another concern. Around 50% of patients reported that price was the main reason they didn’t fill prescriptions for newer oral androgen blockers. While older medications like spironolactone are generally affordable, newer options can be pricey. Consistent use is also critical - missing doses can reduce effectiveness and disrupt hormone balance.
Topical vs. Oral Androgen Blockers: Side-by-Side Comparison
Deciding between topical and oral androgen blockers involves weighing their effectiveness, safety, and convenience to find the best fit for your needs.
Effectiveness and How Fast They Work
Both topical and oral androgen blockers generally take 3 to 6 months to show visible results. However, they differ in how they target the problem.
Topical treatments, like finasteride, act directly on the application site. Research shows that topical finasteride can lower DHT levels in the scalp by 68% to 75%, making it particularly effective for localized concerns like hair loss.
Oral medications, on the other hand, work throughout the body. By entering the bloodstream, they can address multiple androgen-related issues - such as acne, unwanted facial hair, and hair loss - with a single daily dose.
| Feature | Topical | Oral |
|---|---|---|
| Effectiveness | Focused on specific areas (e.g., scalp, face) | Systemic impact across the entire body |
Safety and Side Effects
The safety profiles of topical and oral treatments vary significantly, especially when it comes to side effects.
Topical treatments are generally safer, with side effects limited to the application site. These can include redness, dryness, or mild irritation, affecting about 7% to 17% of users. These reactions are usually mild and manageable.
Oral medications, however, carry more systemic risks. For instance, drugs like flutamide and cyproterone acetate can lead to liver damage, with clinically significant liver injury occurring in 0.1% to 1% of patients on long-term therapy. Minor liver enzyme elevations are more common, seen in 10% to 62% of patients. Additionally, oral contraceptives used in anti-androgen therapy may increase the risk of blood clots, especially in women who smoke, are obese, or are over 39 years old.
"We recommend against the use of flutamide because of its potential hepatotoxicity." - Endocrine Society
Oral spironolactone requires regular blood work to monitor potassium levels and kidney function during the first three months of treatment. In contrast, topical treatments rarely require lab monitoring.
| Side Effect Type | Topical Incidence | Oral Incidence |
|---|---|---|
| Local Reactions | Mild irritation (redness, dryness, itching) | Not applicable |
| Systemic Effects | Rare or negligible | Nausea, mood changes, breast tenderness (20% of users), electrolyte imbalances |
| Serious Risks | Minimal; main concern is accidental transfer to others | Blood clots, liver toxicity, potassium imbalance |
Convenience and Cost
Convenience is another key factor when comparing these treatments.
Oral medications are straightforward - just one pill a day with water. There’s no need for special preparation or extra steps. Topical treatments, like clascoterone cream, usually require twice-daily application to clean, dry skin. This can be time-consuming, and users need to handle the product carefully to avoid accidental transfer to others.
| Aspect | Topical | Oral |
|---|---|---|
| Application | Applied directly to affected areas, often twice daily; requires drying time | Taken once daily with water; no preparation needed |
| FDA Approval Status | Clascoterone (Winlevi) is FDA-approved for acne; some treatments may be compounded | Most options are FDA-approved; some are prescribed off-label |
| Cost Factors | Generally inexpensive, especially with compounded formulations | Affordable options like spironolactone are widely available |
| Lifestyle Impact | May limit activities like swimming due to the risk of secondary exposure | No restrictions on activities or hygiene routines |
sbb-itb-6dba428
How to Choose Between Topical and Oral Androgen Blockers
What to Consider Before Deciding
When deciding between topical and oral androgen blockers, it's essential to weigh several personal factors. If you're dealing with severe hirsutism or haven't seen results with single treatments, a combination therapy - like oral contraceptives paired with an antiandrogen - might be more effective.
Certain health conditions can influence your choice. For instance, oral antiandrogens such as 5-alpha reductase inhibitors should be avoided if you have estrogen-sensitive cancers. Women over 39 or those with obesity should stick to the lowest effective dose to reduce the risk of blood clots. And if you're a smoker, combined oral contraceptives are off the table due to their high clotting risk.
Your daily habits and lifestyle are also important. Topical treatments, like clascoterone cream, require a bit more attention since they need to be applied twice daily. Avoid washing the area right after applying the cream to maintain its effectiveness. If you often have skin-to-skin contact with children or pregnant women, make sure to wash the application site beforehand to prevent hormone transfer. On the other hand, oral medications are easier to incorporate into routines, typically requiring just one pill a day.
Pregnancy is another critical consideration. Antiandrogens are not safe for those who are pregnant, planning to conceive, or breastfeeding. If you’re using only one antiandrogen, you’ll need reliable contraception to prevent risks.
Topical treatments generally come with fewer systemic side effects, mainly causing local irritation. In contrast, oral options can lead to broader side effects, such as nausea, mood swings, and breast tenderness, which affect about 20% of users. Additionally, oral antiandrogens may require regular blood tests to monitor potassium levels and kidney function.
These factors can help you decide whether to start treatment on your own or consult a healthcare provider for guidance.
When to Talk to a Doctor
Before starting any androgen blocker, it’s a good idea to seek professional advice. A doctor can help identify the root cause of your symptoms, often through biochemical tests like serum testosterone measurements. They’ll also check for underlying conditions, such as PCOS or thyroid disorders, which could contribute to hair loss or unwanted facial hair.
"We suggest against antiandrogen monotherapy as initial therapy (because of the teratogenic potential of these medications) unless these women use adequate contraception." - Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline
Your doctor will evaluate any potential risks and ensure you’re using proper contraception if oral antiandrogens are part of your treatment plan. They’ll also monitor for side effects, such as liver issues or electrolyte imbalances, particularly with medications like spironolactone. If your symptoms are moderate to severe or don’t improve after six months, your doctor may adjust your treatment plan or suggest combination therapy.
Androgen Blocker Treatments Through Oana Health
Oana Health provides personalized telehealth solutions for managing androgen-related issues. With just a quick 5-minute online intake, your information is reviewed by licensed U.S. physicians. Once approved, your prescription is shipped to your doorstep for free, complete with automatic refills and ongoing support.
Here’s a closer look at the treatment options available through Oana Health, including both topical and oral formulations.
Topical Treatments: Spironolactone and Eflornithine
For those dealing with localized androgen symptoms, Oana Health offers topical treatments that focus directly on the affected areas, minimizing systemic absorption. One standout option is the Hairless Hype treatment, a combination of three prescription-grade ingredients - Eflornithine, Metformin lotion, and Azelaic Acid. This formula is specifically designed to reduce unwanted facial and body hair growth. Clinical studies show that 81% of women see significant improvement within a year, with some noticing results as early as 8 weeks.
"It's been a little over 5 weeks, and I've noticed a dramatic reduction in my facial hair growth. This has been such a relief for me."
– Allison L., Oana Health Patient
For addressing scalp hair loss, Topical Spironolactone works directly on hair follicles to block androgen activity, avoiding the systemic side effects often associated with oral medications. Pricing begins at $43/month for Topical Spironolactone, while the Hairless Hype treatment starts at $115/month. Both are produced in FDA-regulated compounding pharmacies. Learn more about these treatments at Topical Spironolactone and Eflornithine.
Oral Treatments: Spironolactone and Other Options
For those needing broader symptom management, oral treatments offer systemic relief. Oana Health provides oral androgen blockers tailored for conditions like PCOS. Oral Spironolactone is a commonly prescribed option, with doses ranging from 25–200 mg daily, addressing multiple androgen-related symptoms at once. Another option, the Metformin & Spironolactone Pack, combines insulin sensitization with androgen blocking for a more comprehensive approach to managing PCOS symptoms.
"I used to struggle a lot with the side effects for oral metformin and this is a great alternative for me. I get the same benefits but no more upset stomach and nausea."
– Carrie S., Oana Health Patient
Oral Spironolactone is available starting at $14/month, while the Metformin & Spironolactone Pack starts at $32/month. While effective for systemic symptoms, these treatments require reliable contraception due to potential risks during pregnancy and may involve periodic blood tests to monitor potassium levels and kidney function. Explore these options further at Oral Spironolactone.
Conclusion
Topical treatments are designed to address localized concerns like unwanted facial hair or scalp hair loss. While their effects take longer to appear, they come with fewer systemic side effects. On the other hand, oral medications provide broader antiandrogen benefits, making them suitable for conditions like PCOS, though they carry a higher risk of systemic side effects. Understanding these differences is key to making an informed treatment decision.
It's important to note that both treatment types are not recommended during pregnancy or breastfeeding due to potential risks to the fetus. Factors like age, the severity of hyperandrogenism, and contraceptive needs also influence the choice of treatment. Dr. Andrea Dunaif from Northwestern University emphasizes:
"A 6-month trial is needed to show effects on unwanted hair... The unwanted hair doesn't disappear; it grows in finer and lighter".
Before starting any androgen blocker, consult a healthcare provider to assess hormone levels, rule out contraindications, and create a tailored treatment plan. Regular follow-ups ensure your treatment stays on track and continues to meet your needs.
For those seeking expert guidance, Oana Health offers telehealth consultations with licensed U.S. physicians. They review your medical history and prescribe treatments tailored to you. Options include topical treatments starting at $43/month and oral medications from $14/month, all delivered to your doorstep with free shipping and ongoing support. Learn more at Oana Health.
FAQs
What’s the difference between topical and oral androgen blockers?
Topical androgen blockers come in forms like creams, gels, or patches and are applied directly to the skin. This localized method means less of the drug enters the bloodstream, which helps minimize the risk of systemic side effects, such as sexual dysfunction or cardiovascular problems. In contrast, oral blockers, taken as pills or capsules, circulate through the entire body, offering a more consistent dose but with a higher likelihood of widespread side effects.
In terms of convenience, oral blockers are straightforward - just one pill a day. Topical treatments, however, require more attention, including careful application and measures to prevent the medication from transferring to others through contact. Deciding between the two often comes down to priorities: oral blockers may provide stronger effects, while topical options focus on reducing body-wide side effects.
What’s the difference between topical and oral androgen blockers, and how do I choose the right one?
When deciding between topical and oral androgen blockers, it’s essential to consider your personal needs, lifestyle, and any concerns about potential side effects. Oral blockers are often chosen for their ease of use and consistent daily dosage. However, they may lead to systemic side effects, including hormonal shifts or changes that could affect sexual health.
Topical blockers, by contrast, are applied directly to the skin. This makes them a solid choice if you want to reduce the risk of systemic side effects. They’re especially useful for women or individuals dealing with conditions like hair loss or unwanted facial hair caused by excess androgen activity.
To make the right choice for your situation, it’s important to consult a licensed medical professional. They can guide you based on your specific condition and overall health goals.
What side effects can occur with oral androgen blockers?
Oral androgen blockers can occasionally lead to side effects, which can differ based on the specific medication and how an individual reacts to it. Some of the more commonly reported side effects include fatigue, dizziness, changes in libido, and mood swings. Additionally, these medications may sometimes impact liver function or disrupt electrolyte balance, making it essential to have regular check-ups with a healthcare provider.
If you're thinking about starting oral androgen blockers, it's crucial to talk to a licensed medical professional. They can help you weigh the potential risks and benefits based on your unique health situation.
