How Anti-Androgens Help Female Hair Regrowth
If you're struggling with hair thinning or loss, anti-androgens could be the solution. These medications target hormonal imbalances, particularly elevated androgens like DHT, which are a common cause of female-pattern hair loss. Here's what you need to know:
- What Causes Hair Loss? Hormonal imbalances, especially high DHT levels, shrink hair follicles and disrupt the growth cycle, leading to thinning and shedding.
- How Anti-Androgens Work: They block androgen receptors, reduce androgen production, or inhibit DHT formation to stop hair loss and promote regrowth.
- Common Treatments: Options include oral medications like spironolactone and finasteride, as well as topical solutions for localized effects.
- What to Expect: Results take time - 12 to 24 months for noticeable improvement. Early treatment is key for better outcomes.
Pairing anti-androgens with minoxidil and maintaining a nutrient-rich diet can further improve results. Consult a professional to find the right treatment for your needs.
HORMONES AND HAIR REGROWTH FOR WOMEN| DR DRAY
How Anti-Androgens Promote Hair Regrowth
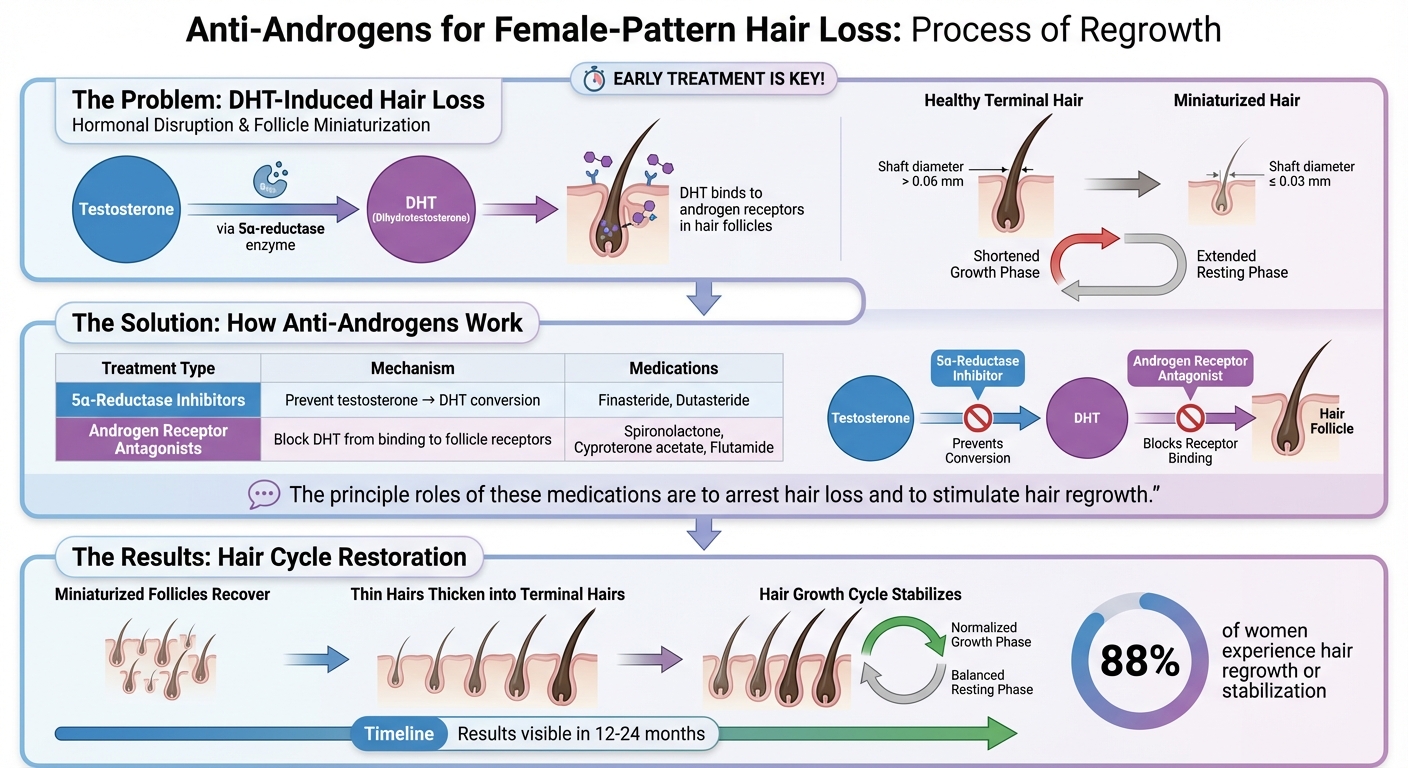
How Anti-Androgens Block DHT and Restore Hair Growth Cycle
Anti-androgens do more than just slow hair thinning - they actively interrupt the hormonal processes that harm hair follicles. By targeting these processes, they create an environment that supports healthier hair growth.
How DHT Causes Hair Loss
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) plays a key role in pattern hair loss, particularly in women. This hormone is created when the enzyme 5α-reductase converts testosterone into DHT. Once formed, DHT binds to androgen receptors in hair follicles, setting off a process known as follicle miniaturization. Dr. Christina Han, MD FRCPC, explains:
"When DHT binds to hair follicle cells, hair follicle miniaturization is initiated. Over time, this process damages hair follicles to the point where they cannot produce healthy hair".
Healthy, terminal hairs generally have a shaft diameter greater than 0.06 mm. However, as miniaturization progresses, the follicles shrink, and the hair diameter can reduce to 0.03 mm or less. DHT also disrupts the natural hair cycle by shortening the growth phase and extending the resting phase, which hampers the regeneration of new hair. Blocking DHT is a critical first step in restoring a healthy hair growth cycle.
| Treatment Category | How It Blocks DHT | Common Medications |
|---|---|---|
| 5α-Reductase Inhibitors | Prevent the conversion of testosterone to DHT | Finasteride, Dutasteride |
| Androgen Receptor Antagonists | Stop DHT from binding to follicle receptors | Spironolactone, Cyproterone acetate, Flutamide |
Restoring the Hair Growth Cycle
By neutralizing DHT's harmful effects, anti-androgens kickstart a reversal process that helps normalize the hair cycle. Medications like finasteride inhibit the conversion of testosterone into DHT, while receptor antagonists such as spironolactone block DHT from attaching to follicles. Together, these actions stop follicle miniaturization, allowing the hair growth cycle to stabilize.
As noted by Leona Yip and Rodney Sinclair:
"The principle roles of these medications are to arrest hair loss and to stimulate hair regrowth".
Over time, miniaturized follicles may recover, with thin, vellus-like hairs thickening into terminal hairs as the growth cycle improves. However, due to the naturally slow pace of hair growth, noticeable results often take 12 to 24 months. While anti-androgens are effective at halting further hair loss and encouraging modest regrowth, they are less likely to produce dramatic restoration. This is why starting treatment early is so crucial - these therapies work best at stabilizing and partially reversing early-stage thinning rather than attempting to regrow hair in areas of advanced baldness.
Common Anti-Androgen Treatments for Hair Regrowth
Anti-androgen medications are commonly used to treat female pattern hair loss (FPHL). These treatments work in different ways to reduce androgen activity at the hair follicle. The choice of medication often depends on factors like the severity of hair loss, other hormonal symptoms, and how well a person tolerates potential side effects.
Spironolactone for Women's Hair Loss
Spironolactone is one of the most prescribed anti-androgen treatments for female hair loss in the United States, though it is used off-label for this purpose. It works by blocking androgen receptors and reducing androgen production from the adrenal glands.
Clinical research supports its effectiveness. For example, a 2024 study conducted at Lahey Hospital & Medical Center treated 62 women with FPHL using low-dose spironolactone (12.5 mg to 50 mg daily). After about a year, participants saw a significant improvement in their Sinclair scale scores - a tool used to measure hair loss severity - dropping from an average of 2.47 to 1.81. Reported side effects were minimal, with only 4.8% of participants experiencing increased urination (polyuria) and another 4.8% reporting lightheadedness.
"Spironolactone has been used off-label in FPHL for over 20 years. It has been shown to arrest hair loss progression with a long-term safety profile." – Plastic Surgery Key
Most women begin to notice thicker hair and less shedding within 3–6 months of starting spironolactone. However, the medication needs to be taken continuously to maintain results, as stopping treatment typically leads to the return of hair loss. For premenopausal women, spironolactone is often paired with oral contraceptives and is strictly avoided during pregnancy due to the risk of feminizing a male fetus.
Oana Health provides spironolactone through licensed professionals, delivering treatments directly to patients' homes.
Other systemic options for FPHL include finasteride, dutasteride, cyproterone acetate, flutamide, and bicalutamide. These medications offer additional choices, but for those seeking less invasive options, topical treatments are worth considering.
Topical vs. Oral Anti-Androgen Options
While oral anti-androgens treat hair loss systemically, topical formulations offer a more localized approach. The decision between the two often depends on the severity of hair loss, tolerance for side effects, and whether other hormonal symptoms, like acne or unwanted facial hair, are present. Oral medications like spironolactone are particularly effective for women dealing with both hair loss and these additional symptoms.
Topical anti-androgens, including topical spironolactone, specifically target androgen receptors in the scalp. This approach minimizes systemic absorption, reducing the likelihood of side effects that affect the whole body while still addressing hair follicle miniaturization. Oana Health also offers topical spironolactone for those who prefer this method. However, topical treatments can cause mild scalp irritation, dryness, or redness and require daily application.
| Feature | Oral Anti-Androgens | Topical Anti-Androgens |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | Systemic: Blocks receptors, reduces androgen production | Local: Targets androgen receptors on the scalp |
| Side Effects | Dizziness, breast tenderness, menstrual changes, electrolyte imbalances | Scalp irritation, dryness, redness; minimal systemic absorption |
| Best For | Moderate-to-severe hair loss or patients with acne/hirsutism | Mild hair loss or patients sensitive to systemic medications |
| Application | Simple daily pill | Requires manual scalp application |
Oral anti-androgens have a long history of use and substantial clinical evidence behind them, making them the go-to treatment for many women with FPHL. On the other hand, topical options are becoming increasingly popular, especially for those who cannot tolerate oral medications or have milder hair loss. Both types of treatments are often combined with topical minoxidil to tackle hair loss from multiple angles and improve regrowth outcomes.
sbb-itb-6dba428
Combining Anti-Androgens with Other Hair Loss Treatments
Anti-androgen therapy works best when it's part of a broader hair treatment plan. While anti-androgens help block DHT and slow down hair loss, pairing them with other treatments can address multiple factors affecting hair health. Let’s explore some combination strategies that can amplify the effectiveness of anti-androgen therapy.
Using Minoxidil with Anti-Androgens
One of the most effective approaches for promoting hair regrowth, especially in women, is combining anti-androgens with minoxidil. These two treatments work in entirely different ways, creating a complementary effect. Anti-androgens such as spironolactone prevent DHT from shrinking hair follicles, while minoxidil improves blood flow to the scalp and prolongs the active growth phase of hair follicles.
"Minoxidil lotion has been shown to be effective in treating androgenetic alopecia. Its effects are nonandrogen-mediated and this agent can be combined with antiandrogen therapy for an additive effect." – Rodney D. Sinclair, Professor of Dermatology
This combination tackles hair loss from two angles: addressing the hormonal cause with anti-androgens and stimulating follicle health and growth with minoxidil. Research shows that about 40% of patients experience noticeable improvement using 5% topical minoxidil alone. Adding an anti-androgen can significantly enhance these results, especially for women who haven’t responded well to minoxidil on its own.
A well-documented and effective regimen includes 0.25 mg of oral minoxidil combined with 25 mg of spironolactone. For those who experience irritation from topical minoxidil, switching to the 5% foam version can help. The foam formulation typically excludes propylene glycol, a common irritant in liquid versions.
Keep in mind, both treatments require consistent use. Stopping either one can lead to renewed hair shedding within 4 to 6 months. Additionally, women of reproductive age using anti-androgens must take highly effective oral contraceptives to prevent birth defects.
Diet and Lifestyle Factors for Hair Health
Medications are only part of the solution - diet and lifestyle choices also play a crucial role in supporting hair health. Eating a balanced diet rich in lean proteins, complex carbohydrates, fruits, and vegetables can help maintain hormonal balance and supply the nutrients needed for keratin production. Nutrients like zinc, biotin, and iron are particularly important, and studies suggest that anti-androgen therapy works better when ferritin (iron) levels are above 40 μg/l.
Healthy habits can further support hair regrowth. Scalp massages, for instance, improve blood flow to hair follicles and may help with androgenic alopecia symptoms. Gentle hair care and avoiding tight hairstyles reduce unnecessary stress on the hairline. Poor sleep can disrupt melatonin and serotonin levels, potentially worsening conditions like PCOS that contribute to hair thinning. Additionally, 2% ketoconazole shampoo (Nizoral) offers anti-inflammatory and mild anti-androgenic benefits, which can complement systemic treatments.
Before starting any treatment, it’s a good idea to check for underlying issues like iron deficiency, low vitamin D, or thyroid problems, as these can worsen hair loss. Combining targeted medications with healthy lifestyle adjustments creates a well-rounded approach to improving hormonal balance and encouraging hair regrowth.
What to Expect: Results and Side Effects
Let’s dive into what you can anticipate regarding hair regrowth timelines and how to handle potential side effects during your treatment journey.
Timeline for Seeing Hair Regrowth Results
Patience is crucial when starting anti-androgen therapy for hair regrowth. Significant changes typically take time, with noticeable improvements appearing between 12 and 24 months as miniaturized hair follicles begin to recover. In the early stages - usually within the first 2 to 8 weeks - you might notice increased shedding. While this can feel discouraging, it’s actually a sign that weaker hairs are making way for healthier regrowth.
"An initial therapeutic response often takes 12 or even 24 months. Given this delay, monitoring for treatment effect through clinical photography or standardized clinical severity scales is helpful." – Rodney Sinclair, Professor of Dermatology, University of Melbourne
To track progress, consider using clinical photographs or standardized scales like the Sinclair or Ludwig scales. These tools can help you see improvements that might not be obvious day-to-day.
It’s important to set realistic expectations. Anti-androgen treatments are generally better at halting further hair loss than at producing dramatic new growth. For example, a study found that about 88% of women using spironolactone or cyproterone acetate experienced either hair regrowth or stabilization of hair loss. However, because female pattern hair loss is a chronic condition, ongoing treatment is necessary to maintain results.
Managing Side Effects of Anti-Androgens
Like most medications, anti-androgens come with potential side effects. Common ones include menstrual irregularities, breast tenderness, dizziness, fatigue, and nausea. To reduce risks, it’s best to start with a low dose and gradually increase it while monitoring blood pressure and electrolyte levels.
Specific medications have their own side effects. Cyproterone acetate, for example, can lead to weight gain, depression, tiredness, and breast tenderness. Combining it with oral contraceptives can help regulate menstrual cycles and prevent pregnancy. Flutamide, another option, carries a small risk of liver dysfunction (about 3 in 10,000 users), so regular liver function tests are essential. Women of childbearing age must use reliable contraception while on these treatments.
If you’re using topical minoxidil alongside anti-androgens and experience scalp irritation - a common issue for about 82% of users due to the propylene glycol in the solution - switching to a 5% foam formulation can often resolve the problem.
Regular follow-ups with your healthcare provider are key. These check-ins help fine-tune your treatment plan and address any side effects that may arise.
Conclusion: Starting Your Hair Regrowth Journey
Anti-androgen medications work by blocking DHT, helping to restore the hair growth cycle and prevent further thinning. When combined with minoxidil, this approach has been shown to be highly effective for many women dealing with female-pattern hair loss. As Dr. Elise A. Olsen from Duke University Medical Center explains:
"Antiandrogen agents or 5α-reductase inhibitors are effective treatments in women with female-pattern hair loss and are useful in combination with minoxidil." – Elise A. Olsen, M.D.
The journey to effective treatment begins with a professional evaluation to determine the best anti-androgen therapy for your unique needs.
If you're ready to take the next step, Oana Health provides accessible telehealth consultations with licensed medical professionals who specialize in hormonal hair loss. Their services include personalized treatment plans tailored to your situation, offering options like oral spironolactone starting at $14/month, topical spironolactone at $43/month, or oral minoxidil at $25/month - all delivered straight to your door. Start your hair regrowth journey today by scheduling a telehealth consultation with a licensed expert.
FAQs
How do anti-androgens help with hair regrowth in women?
Anti-androgens tackle hair loss by targeting DHT (dihydrotestosterone), a hormone known to shrink hair follicles and cause thinning. These medications work in one of two ways: they either block the enzyme 5α-reductase, which is responsible for converting testosterone into DHT, or they stop DHT from attaching to androgen receptors in the hair follicles.
By minimizing DHT's impact, anti-androgens can help slow down follicle shrinkage, support healthier hair growth, and gradually improve hair density. This approach is particularly beneficial for women dealing with hair loss linked to hormonal imbalances.
What side effects can anti-androgens cause when treating hair loss in women?
Anti-androgens may lead to side effects like menstrual irregularities, fatigue, or occasional mild dizziness. These effects can differ from person to person but are often manageable with proper medical guidance.
Discussing the potential benefits and risks with a licensed healthcare provider is essential to determine if this treatment aligns with your needs. Open communication ensures you make an informed decision.
Can anti-androgens and minoxidil be used together for better hair regrowth results?
Yes, using a combination of spironolactone and minoxidil can improve hair regrowth for women dealing with hair loss. Spironolactone, an anti-androgen, blocks dihydrotestosterone (DHT) - a hormone responsible for shrinking hair follicles. Meanwhile, minoxidil boosts blood flow to the scalp and prolongs the hair growth cycle. Together, these treatments tackle both hormonal and follicle-related causes of hair loss, often resulting in thicker hair, less shedding, and better overall density. Many women notice visible improvements within 4–6 months of consistent use.
However, both treatments can come with side effects. Minoxidil may cause scalp irritation, while anti-androgens like spironolactone can lead to menstrual changes. Because of this, it’s essential to use these treatments under a doctor’s guidance. Telehealth services like Oana Health can help by creating tailored treatment plans, prescribing appropriate doses, and even delivering medications to your doorstep. To maintain progress, sticking to the treatment plan is crucial, as stopping could undo the benefits.
