Minoxidil for Women: What to Expect After 1 Year
Minoxidil is the only FDA-approved medication proven to regrow hair in women. Over a year of consistent use, women can see a 14–18% increase in scalp hair density and reduced hair loss. However, results take time, and early shedding is common as dormant follicles are reactivated. Here's a quick breakdown of what to expect:
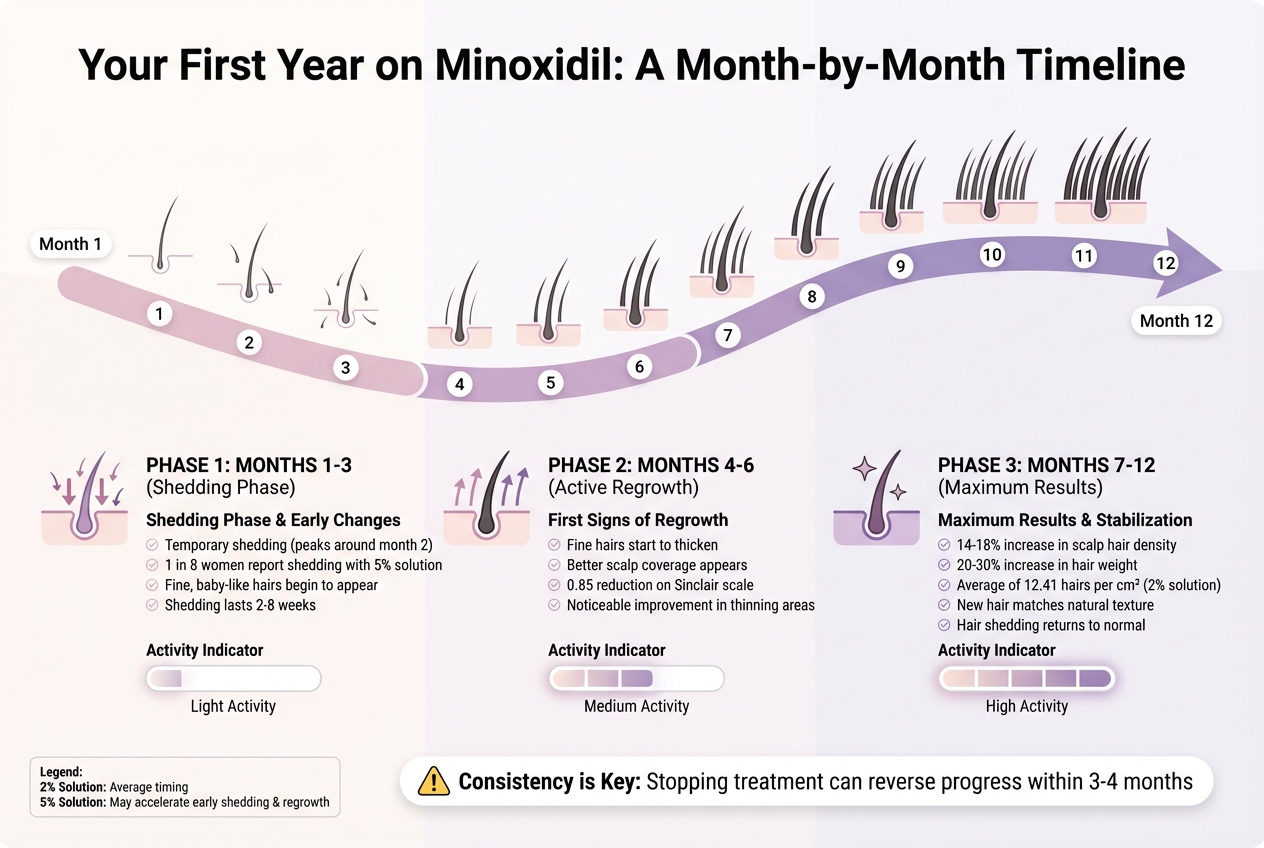
- Months 1–3: Temporary shedding occurs as hair enters a new growth phase. Fine, soft hairs begin to appear.
- Months 4–6: Regrowth becomes noticeable. Thin hairs start to thicken, providing better coverage.
- Months 7–12: Hair density peaks, with new growth resembling your natural texture. Results stabilize, and hair loss slows significantly.
Consistency is key - missing applications or stopping treatment can reverse progress within months. While comparing 2% vs 5% minoxidil shows the 5% foam delivers faster results, the 2% solution is gentler for sensitive scalps. Always consult a healthcare provider to confirm if minoxidil suits your hair loss type.
Minoxidil Hair Regrowth Timeline: What to Expect in Your First Year
WHAT MY HAIR LOSS LOOKS LIKE AFTER ONE YEAR OF ROGAINE FOAM FOR WOMEN (Check out this growth!)
How Minoxidil Works for Women
Minoxidil helps combat hair loss by revitalizing hair follicles through a variety of biological processes. It acts as a vasodilator, meaning it widens the blood vessels in the scalp, improving blood flow. This enhanced circulation brings oxygen, nutrients, and growth factors directly to the hair follicles, which can reverse the miniaturization process responsible for thinning hair.
Additionally, minoxidil prolongs the anagen phase - the active growth stage in the hair cycle. This extension allows hair strands to grow thicker and longer before they naturally shed. On a cellular level, it activates specific potassium channels in follicle cells, further stimulating hair growth activity.
One key reason minoxidil is well-suited for women is its non-hormonal mechanism. In a study involving 984 participants over one year, 62% experienced a reduction in hair loss-affected areas, while about 32% noticed visible cosmetic improvements and regrowth of terminal hair. These results highlight which candidates are likely to benefit most from the treatment.
Who Should Use Minoxidil?
Knowing how minoxidil works helps identify who will see the most benefit. The treatment is particularly effective for androgenetic alopecia, the most common type of hair loss in women, affecting roughly 40% of women by the age of 50. Starting minoxidil early - during the initial to moderate stages of hair thinning - can increase its effectiveness by 46%.
Before beginning treatment, it's important to consult a healthcare provider to confirm your type of hair loss. Minoxidil is not effective for conditions like sudden or patchy hair loss, deficiencies in nutrients like iron or vitamin D, or hair loss linked to thyroid issues. Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding should avoid using minoxidil, as it is not considered safe during these times.
If your hair loss is accompanied by other symptoms such as irregular periods, weight fluctuations, or unwanted facial hair, it could indicate an underlying condition. In these cases, Oana Health (https://oanahealth.com) provides telehealth consultations with licensed professionals who can assess your situation and, if appropriate, prescribe personalized treatments delivered straight to your door.
What to Expect During Your First Year on Minoxidil
Understanding the timeline of minoxidil treatment can help you stay committed by knowing what changes to anticipate at each stage.
Months 1–3: Shedding Phase and Early Changes
In the first few weeks (typically between 2–8 weeks), many users notice temporary hair shedding. This happens because minoxidil stimulates hair follicles to shift from a resting phase to an active growth phase. Shedding often peaks around the second month, with about 1 in 8 women using a 5% solution reporting this effect during the early stages. While it may seem alarming, this shedding is actually a sign that minoxidil is working to activate new hair growth.
"Minoxidil (Rogaine) can cause temporary hair shedding, often called 'minoxidil shedding,' as it pushes out old hairs to make way for new growth",
explains Dr. Maybell Nieves.
This shedding phase usually lasts 2 to 8 weeks. By the second or third month, many women start noticing fine, baby-like hairs appearing in areas where hair was thinning. During this time, it’s essential to be gentle with your hair - avoid harsh chemicals or tight hairstyles that could add stress. Stick to the application instructions, such as using a 2% solution twice daily, to ensure your follicles consistently receive the treatment. Once the shedding subsides, you’ll start to see the first signs of regrowth.
Months 4–6: First Signs of Regrowth
After the initial shedding phase, the real progress begins. By this time, regrowth enters its active phase, and the fine, soft hairs that appeared earlier start to thicken and strengthen. This provides more noticeable coverage in areas previously experiencing hair loss. Research indicates that women typically see a reduction in hair loss severity by about 0.85 on the Sinclair scale after six months of consistent use.
Consistency is key during this period. Missing applications can slow down progress, so make sure you’re applying minoxidil daily. For the best results, gently massage the product into your scalp and allow it to fully dry before styling. Tracking your progress can also help keep you motivated as you notice these early improvements. Over time, these fine hairs will continue to grow thicker, setting the stage for even more substantial results in the months ahead.
Months 7–12: Maximum Results and Stabilization
By the time you reach the one-year mark, the full effects of minoxidil become apparent. Women often experience a 14%–18% increase in scalp hair and a 20%–30% rise in hair weight, depending on the concentration of the solution used. Clinical studies show an average increase of 12.41 hairs per square centimeter for those using the 2% solution.
At this stage, your hair growth cycle stabilizes. The new hairs that initially felt soft and downy will now have a texture similar to your existing hair. The focus shifts from growing new hair to maintaining the gains you’ve achieved. Hair shedding typically returns to normal levels, signaling that the treatment has reached its full potential.
"A 14% to 18% increase in scalp hair is the expected outcome at 1 year of treatment in women. Similarly, the peak effect of minoxidil appears to occur at about 1 year of treatment",
notes Dr. Lilian White.
To maintain these results, it’s crucial to continue daily use of minoxidil. Stopping the treatment will likely result in losing the newly regrown hair within 3 to 4 months as your hair reverts to its natural growth cycle.
sbb-itb-6dba428
2% vs. 5% Minoxidil: Which Concentration to Choose
Once you've tracked your progress over the year and noticed visible regrowth, the next important step is deciding which minoxidil concentration fits your needs best.
Both the 2% solution and the 5% foam have FDA approval, but they differ in how often you need to apply them, how effective they are, and the likelihood of side effects. The 2% solution requires application twice a day, while the 5% foam is designed for a more convenient once-daily use. For many women with packed schedules, this makes the 5% foam a more practical choice.
When it comes to results, the 5% concentration generally delivers quicker and more noticeable improvements. Clinical studies report that over 80% of women using the 5% foam experienced hair regrowth within six months. In contrast, only 19% of women using the 2% solution reported moderate regrowth after eight months, with 40% seeing only minimal improvement. Additionally, women using the 5% solution achieved better scalp coverage and increased hair density, according to multicenter studies.
"Women using the 5% solution achieved the most significant results, while the 2% solution also outperformed the placebo group",
explains Dr. Epameinondas Bonaros, Hair Transplant Surgeon.
However, the 5% concentration isn't without drawbacks. It comes with a higher likelihood of scalp irritation and itching, and there's an increased risk of unwanted facial hair growth if the product accidentally transfers to other areas. For women with sensitive scalps or mild thinning, the 2% solution is often a gentler option.
If you’re dealing with general thinning at the top of the scalp, the 5% foam is typically the better choice, thanks to its stronger effectiveness and once-a-day application. On the other hand, if your hair loss is mild or you have a sensitive scalp, starting with the 2% solution might be a better way to assess your tolerance before moving to a higher concentration.
Comparison Table: 2% vs. 5% Minoxidil
| Feature | 2% Minoxidil (Solution) | 5% Minoxidil (Foam) |
|---|---|---|
| Application Frequency | Twice daily | Once daily |
| Time to First Results | 4–8 months | 3–6 months |
| Clinical Efficacy | 19% moderate regrowth at 8 months | Over 80% saw regrowth |
| Common Side Effects | Scalp irritation, dryness | Higher risk of itching, unwanted facial hair |
| Best For | Mild thinning, sensitive scalps | General thinning at the top of the scalp |
| Price | Two-month supply (generic) | $49.97 for 2-month supply |
Maintaining Results and Managing Side Effects
Hitting the one-year mark with minoxidil is a big deal - it shows your commitment to hair regrowth. But keeping those results depends on sticking to the treatment. If you stop using minoxidil, the progress you’ve made can start to reverse.
Within one to two weeks of stopping, the blood vessels in your scalp may begin to narrow, cutting off some of the oxygen and nutrients your hair follicles need. By the three-to-six-month mark, you could see more shedding, and in some cases, hair density might drop below what it was before you started treatment.
"Think of it like pausing a clock – when you stop minoxidil, the clock starts ticking again from where it naturally would have been."
- Dr. Suhail Alam, Medical Director, Aventus Clinic
The good news is that minoxidil has long been proven safe for extended use, with nearly 40 years of clinical data backing it up. If you’re considering switching to something like oral minoxidil, talk to a healthcare professional first to ensure a smooth transition.
What Happens If You Stop Using Minoxidil?
Stopping minoxidil triggers a predictable chain of events. In the first two weeks, blood flow to your follicles starts to decrease. Soon after, shedding becomes noticeable, and hair density begins to thin. By the three-to-six-month point, your hair growth cycle will likely return to the way it was before treatment.
"If you stop using it, the normal hair loss process will start again. You will probably lose your newly regrown hair within 3 to 4 months."
- Rogaine Official FAQ
Without minoxidil, hair loss can progress to where it would have naturally been if you’d never started. If you decide to restart treatment later, expect to wait another four to six months to see noticeable results. For anyone transitioning to a different hair loss solution, overlapping the treatments for two to three months can help minimize sudden shedding.
How to Manage Common Side Effects
While tracking your progress, it’s also important to address any side effects that might come up.
Most minoxidil-related issues, like scalp irritation, redness, or itching, can be managed with a few simple tweaks:
- Make sure your scalp is completely dry before applying minoxidil, and consider using a mild, pH-balanced shampoo.
- Switching to the foam version may help, as it’s often easier on the scalp and less likely to drip or cause irritation.
- For persistent flaking, try a ketoconazole shampoo to calm the irritation.
To avoid unwanted facial hair growth, wash your hands thoroughly after applying minoxidil and apply it at least two to four hours before bedtime. A silk pillowcase can also reduce friction and protect fragile new growth.
Though systemic side effects are rare, be on the lookout for symptoms like chest pain, rapid heartbeat, dizziness, or unexplained weight gain. If you experience any of these, stop using minoxidil immediately and consult your healthcare provider. While about 1% of users stop treatment due to side effects, most women tolerate it well when used as directed.
If you don’t see any progress after four to six months of consistent use or if side effects become unmanageable, it’s time to consult a medical professional. Platforms like Oana Health offer telehealth appointments with licensed providers who can evaluate your treatment plan and discuss alternatives like topical spironolactone or oral minoxidil.
Is Minoxidil Right for You?
Minoxidil is most effective for women experiencing androgenetic alopecia, which is hereditary thinning along the top of the scalp. Starting treatment early can improve results by up to 46%. However, if your hair loss is sudden, patchy, or caused by factors like childbirth, nutrient deficiencies, or thyroid issues, minoxidil may not be the right solution.
It’s important to understand that minoxidil requires time and commitment. The full benefits often take up to a year of consistent use, with clinical studies showing a 14% to 18% increase in scalp hair over that period. But keep in mind, stopping the treatment can lead to losing the progress made within a few months.
"Minoxidil treatment tends to work best for those in the earlier stages of hair thinning and hereditary hair loss."
- Dr. Epameinondas Bonaros, Hair Transplant Surgeon
Before starting minoxidil, take a close look at your health history. It’s not recommended for pregnant or breastfeeding women, those with heart conditions, or anyone under 18. Also, make sure to apply it only on a healthy scalp, avoiding areas that are red, inflamed, or irritated.
To ensure minoxidil is a good fit for your situation, consult with a healthcare provider. They can help identify whether your hair loss pattern is suitable for this treatment or if other options might work better. For personalized advice, platforms like Oana Health offer telehealth consultations with medical professionals who can guide you through treatments, including topical or oral minoxidil.
FAQs
What should I do if I experience side effects while using minoxidil?
If you notice side effects like scalp irritation, redness, itching, unwanted facial hair growth, swelling in your hands or feet, chest pain, rapid heartbeat, dizziness, fainting, or sudden weight gain, stop using minoxidil right away. Rinse the affected area with cool water and reach out to a healthcare professional promptly to discuss your symptoms and consider other treatment options.
For more serious symptoms - like chest pain, fainting, or noticeable swelling - seek medical attention immediately. Additionally, if you don’t see any hair regrowth after using minoxidil consistently twice a day for about four months, it’s worth consulting a healthcare provider to evaluate your progress and adjust your approach.
With Oana Health, you can easily schedule a telehealth visit with a licensed professional. They can assess your symptoms, tweak your treatment plan, or recommend alternative therapies. Plus, medications are shipped directly to your door for free, making it simple to get the care you need without added stress.
How long does it take to see results from minoxidil?
Most women start to see visible hair regrowth around 8 weeks with daily use, but consistency is crucial. Typically, full results take about 3 to 4 months of regular application.
It's worth noting that everyone's experience may differ, so patience is essential when using minoxidil. To get the best results, always stick to the recommended application guidelines.
Can I use minoxidil if I have other health conditions?
Minoxidil is considered safe for many women, but if you have existing health issues, such as heart disease, it's crucial to consult your doctor before beginning treatment. Should you notice severe symptoms like chest pain, a fast heartbeat, swelling, or trouble breathing while using minoxidil, stop using it right away and seek medical help.
Your well-being should always be the top priority. Talking openly with a licensed healthcare provider about your medical history can help determine whether minoxidil is a suitable choice for you.
