Spironolactone vs. Eflornithine: Drug Interactions
Spironolactone and Eflornithine are two medications often used to manage PCOS symptoms and facial hirsutism, but they work very differently. Spironolactone is a systemic oral medication that blocks androgen effects and can interact with many drugs, especially those affecting potassium levels. In contrast, Eflornithine is a topical cream with minimal absorption, leading to fewer interaction risks. Here's a quick breakdown:
- Spironolactone: Effective for hormonal acne, excessive hair growth, and PCOS-related symptoms. However, it requires regular blood tests due to risks like hyperkalemia (high potassium levels) and interactions with ACE inhibitors, NSAIDs, and potassium supplements.
- Eflornithine: Slows facial hair growth without altering hormones. Its localized action means fewer interactions, but it may cause skin irritation if not applied correctly.
Quick Comparison
| Feature | Spironolactone (Oral) | Eflornithine (Topical) |
|---|---|---|
| How It Works | Blocks androgens systemically | Inhibits hair growth locally |
| Absorption | High (>90%) | Minimal |
| Drug Interactions | High risk (e.g., ACE inhibitors, NSAIDs) | None reported |
| Monitoring | Requires blood tests | Not required |
| Key Concern | Hyperkalemia | Skin irritation |
Both medications can be combined for tailored treatment, but understanding their differences ensures safer and more effective use. Always consult a healthcare provider to determine the best option for your needs.
Spironolactone Drug Interactions
Spironolactone, due to its systemic effects, carries several drug interaction risks. One of the most serious is hyperkalemia, or elevated potassium levels. This is especially relevant for women managing PCOS, as they may already be taking multiple medications.
Interactions with Diuretics, ACE Inhibitors, and Potassium-Altering Drugs
Because Spironolactone affects potassium levels, it needs to be used cautiously with other medications that do the same. Combining it with ACE inhibitors (like lisinopril), angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), potassium-sparing diuretics, or potassium supplements can significantly increase the risk of severe hyperkalemia. It is particularly dangerous to use Spironolactone alongside eplerenone, as this combination poses an extreme risk for dangerously high potassium levels.
In certain cases, such as heart failure, low doses of Spironolactone may be safely used with ACE inhibitors, but only if potassium levels are closely monitored. Doctors typically check potassium levels within a week of starting or adjusting the dose and may pause or reduce the medication if levels exceed 5.5 mEq/L. Patients are advised to avoid potassium salt substitutes and limit foods high in potassium.
Interactions with NSAIDs, Steroids, and Alcohol
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen and naproxen, can interfere with Spironolactone's effects. They may reduce its diuretic and blood pressure-lowering benefits while increasing the risk of hyperkalemia and kidney problems. Aspirin can also disrupt Spironolactone's effectiveness by reducing the secretion of its active metabolite, which might require a dosage adjustment.
When used with corticosteroids or ACTH, Spironolactone may cause additional electrolyte imbalances, particularly affecting potassium levels. Alcohol adds another layer of concern by increasing the risk of orthostatic hypotension - dizziness when standing up - which raises the likelihood of falls. Patients who drink alcohol should do so in moderation and be cautious when changing positions.
Extra care is needed for individuals taking lithium, as Spironolactone can reduce lithium's clearance from the body, increasing the risk of toxicity. Regular monitoring of lithium levels is essential when these two medications are used together. These potential interactions highlight the importance of careful medication management and close monitoring when using Spironolactone.
Eflornithine Drug Interactions
Eflornithine stands apart from treatments like spironolactone due to its unique interaction profile. As a topical, non-hormonal, and non-systemic prescription option for women managing facial hirsutism, it works locally, avoiding systemic distribution entirely. This distinct mode of action contributes to its specific safety characteristics.
Minimal Systemic Absorption and Interaction Risk
Eflornithine works by inhibiting a natural substance in hair follicles that promotes hair growth. Since it’s applied topically and absorbed minimally into the bloodstream, it doesn’t interact with medications such as ACE inhibitors, NSAIDs, or potassium supplements. To date, no significant systemic drug interactions have been reported. Overdose risks are also extremely low unless the cream is over-applied or ingested.
Although systemic concerns are minimal, proper application is essential to avoid localized issues.
Combining Eflornithine with Other Topical Products
Because eflornithine is applied directly to the skin, the primary concerns are local side effects, such as irritation. However, it can be safely used alongside cosmetics or sunscreens, provided the cream has fully dried beforehand.
For best results, follow these guidelines:
- Wait at least 5 minutes after hair removal before applying the cream to reduce irritation.
- Avoid washing the treated area for at least 4 hours after application to ensure the cream is fully absorbed.
- Apply the cream twice daily, ensuring there’s an 8-hour gap between applications.
If you experience skin irritation or a rash, consult your doctor. In severe cases, discontinuation may be necessary.
Side-by-Side Comparison of Interaction Risks
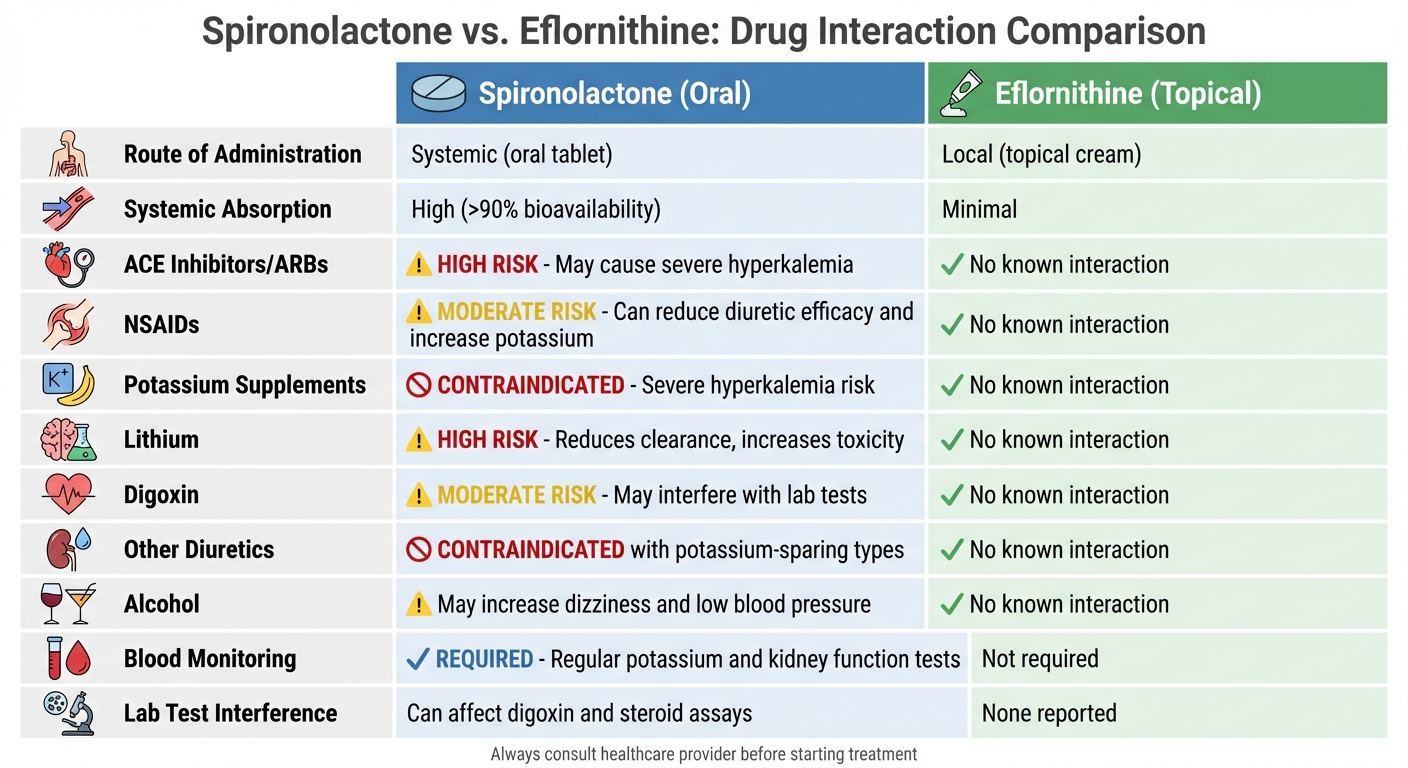
Spironolactone vs Eflornithine Drug Interactions Comparison Chart
When treating hirsutism, it's crucial to understand how different medications interact with other drugs and the body. Spironolactone, which is absorbed systemically at a high rate (>90%), carries a greater risk of interactions. In contrast, eflornithine, applied topically, has minimal systemic absorption, significantly reducing its interaction risks. Due to its systemic effects, spironolactone often requires regular blood tests to monitor potassium levels and kidney function. Patients are also advised to avoid potassium supplements or other potassium-rich agents. On the other hand, eflornithine's concerns are largely limited to potential skin irritation rather than systemic complications.
Table: Spironolactone vs. Eflornithine Drug Interaction Comparison
| Interaction Category | Spironolactone (Oral) | Eflornithine (Topical) |
|---|---|---|
| Route of Administration | Systemic (oral tablet) | Local (topical cream) |
| Systemic Absorption | High (>90% bioavailability) | Minimal |
| ACE Inhibitors/ARBs | High risk – may cause severe hyperkalemia | No known interaction |
| NSAIDs | Moderate risk – can reduce diuretic efficacy and increase potassium levels | No known interaction |
| Potassium Supplements | Contraindicated – severe hyperkalemia risk | No known interaction |
| Lithium | High risk – reduces clearance and increases toxicity | No known interaction |
| Digoxin | Moderate risk – may interfere with lab tests | No known interaction |
| Other Diuretics | Contraindicated with potassium-sparing types | No known interaction |
| Alcohol | May increase dizziness and low blood pressure | No known interaction |
| Blood Monitoring | Regular monitoring required for potassium and kidney function | Generally not required |
| Lab Test Interference | Can affect digoxin and steroid assays | None reported |
This comparison shows why healthcare providers might lean toward eflornithine for patients worried about drug interactions. However, spironolactone remains a preferred choice for addressing broader PCOS symptoms, such as acne and more widespread hirsutism. These distinctions play a significant role in shaping treatment plans and monitoring strategies for PCOS and hirsutism.
sbb-itb-6dba428
Clinical Considerations for Safe Use
Monitoring Requirements
Spironolactone requires close monitoring of serum potassium levels and kidney function. Testing is recommended within 2–3 days of starting treatment, again at 7 days, then monthly for the first three months, and every three months afterward. Despite these guidelines, adherence is low - only 5.5% of 33,234 women had potassium levels checked within the first week, and just 31.1% underwent at least one test during treatment. Interestingly, women aged 45 and older were more likely to receive proper monitoring (43.3%) compared to younger women aged 12 to 19 (22.4%).
"This underscores the need for updated guidelines and better education on timely potassium testing to enhance patient safety and care quality." - Dr. Philip Tong, Expert Dermatologist and Co-Chair of the All About Acne board
Patients should stay alert for signs of hyperkalemia, such as muscle weakness, fatigue, irregular heartbeat, or heart palpitations. Those with kidney issues, heart conditions, or who are taking medications like ACE inhibitors or NSAIDs need extra caution. Regular blood pressure monitoring is also essential, often on a monthly basis, until stable. While spironolactone requires this intensive oversight, eflornithine offers a more straightforward approach.
Thanks to its minimal systemic absorption, eflornithine does not require routine blood tests. Monitoring is limited to watching for local skin reactions, such as stinging or acne at the application site. For optimal results, patients should apply the cream at least five minutes after hair removal and avoid washing the area for four hours to ensure proper absorption. These tailored monitoring strategies highlight the importance of individualized care, balancing effectiveness with safety - an approach central to Oana Health's treatment philosophy.
PCOS and Hirsutism Treatment at Oana Health
Oana Health provides personalized telehealth treatment plans designed to prioritize safety and precision for women managing PCOS and hirsutism. Their platform offers both spironolactone and eflornithine, with licensed professionals reviewing each patient’s medical history to recommend the most suitable option. Whether it’s systemic therapy with spironolactone ($14/month), topical treatment with eflornithine ($69/month), or a combination approach, the focus is on tailoring care to individual needs.
For spironolactone users, Oana Health coordinates all required lab work, ensuring seamless monitoring. Eflornithine users receive clear guidance on application techniques to maximize effectiveness. Treatments are shipped directly to patients’ homes with free delivery, and the medical team remains readily available to address concerns about side effects, drug interactions, or adjustments to therapy. This all-in-one support system simplifies care, making it easier for women to stay on top of their treatment without juggling multiple appointments.
Conclusion
Spironolactone and eflornithine offer different approaches to managing PCOS and hirsutism, each with unique considerations for drug interactions. Spironolactone, being a systemic medication, comes with a notable risk of drug interactions, particularly the possibility of severe hyperkalemia. This makes regular blood tests and close coordination with healthcare providers essential. On the other hand, eflornithine, applied topically, has minimal systemic absorption, which significantly reduces the likelihood of drug interactions.
When deciding on treatment, individual circumstances play a crucial role. Women who take multiple medications or have kidney-related concerns might find eflornithine’s localized action more suitable. Meanwhile, those looking for hormonal benefits may lean toward spironolactone, provided they can manage the necessary monitoring. With PCOS affecting about 20% of women during their reproductive years, understanding these differences ensures a more tailored and safer treatment plan.
For personalized care, consulting licensed professionals is key. Oana Health’s telehealth platform offers expert guidance by reviewing your medical history and current medications. They can recommend either spironolactone (available at $14/month) or eflornithine (offered at $69/month), ensuring your treatment aligns with your health needs and minimizes potential risks.
FAQs
What are the key differences in drug interactions between spironolactone and eflornithine?
Spironolactone is well-known for its interaction with various drugs and supplements, while the interaction profile for eflornithine remains less explored in available data. Spironolactone can raise potassium levels, which may lead to severe hyperkalemia when combined with potassium supplements, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin-receptor blockers, NSAIDs, heparin, or trimethoprim. Additionally, it can reduce the clearance of lithium, increasing the risk of lithium toxicity, and may interfere with digoxin test results. Because of these risks, regular monitoring of electrolytes, lithium levels, and overall drug effectiveness is crucial when using spironolactone.
On the other hand, eflornithine has limited information regarding its interactions with other drugs or supplements. The data available suggests that its interaction profile is either minimal or not well-documented. This makes spironolactone’s interactions more clinically relevant and something that requires close attention.
For safe, prescription-based treatments addressing concerns like unwanted facial hair or hormonal imbalances, Oana Health provides personalized telehealth services led by licensed medical professionals.
Why does spironolactone require regular monitoring while eflornithine does not?
Spironolactone needs careful oversight because it can raise potassium levels in the blood. If unchecked, this can result in hyperkalemia or other health issues. Additionally, it may interact with other medications, making regular lab tests crucial to ensure its safe administration.
On the other hand, eflornithine is a topical treatment that stays mostly on the skin with minimal absorption into the bloodstream. Since it works on the surface and doesn't significantly impact internal systems, routine lab tests aren't required when using it.
How do spironolactone and eflornithine work together to manage PCOS-related hirsutism?
Spironolactone and eflornithine work well together in managing hirsutism linked to PCOS because they tackle different aspects of the condition.
Spironolactone is an oral medication that blocks androgen receptors and lowers androgen levels in the body. This helps address hormonal imbalances responsible for excess hair growth, acne, and other PCOS-related symptoms.
Meanwhile, eflornithine is a topical cream that targets facial hair by slowing its growth. It works by inhibiting a specific enzyme in hair follicles.
By combining the systemic hormonal benefits of spironolactone with the localized effects of eflornithine, this approach offers a more thorough way to manage PCOS-related hirsutism, particularly for facial hair concerns.
