Synbiotics and Insulin Resistance in PCOS
Insulin resistance impacts 50–80% of women with PCOS, regardless of weight. This metabolic issue worsens symptoms like irregular cycles, acne, and hair growth, while increasing risks of diabetes and heart disease. Standard treatments like metformin help some women but often fall short or cause side effects.
Emerging research highlights synbiotics - a mix of probiotics and prebiotics - as a promising option. These supplements improve gut health, reduce inflammation, and enhance insulin sensitivity. Studies show they can lower fasting insulin, HOMA-IR scores (a marker of insulin resistance), and cholesterol levels, with minimal side effects. Combining synbiotics with metformin may boost results further.
For best results:
- Look for multi-strain synbiotics with Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium.
- Use at least 4 billion CFU/day with prebiotics like inulin for 8–12 weeks.
- Pair with standard treatments and consult a healthcare provider.
This integrated approach may offer better management of PCOS symptoms and metabolic health.
Insulin Resistance and PCOS | Insulin resistant PCOS, symptoms, and how to manage it
How Insulin Resistance Affects Women with PCOS
Insulin resistance impacts a staggering 50–80% of women with PCOS, cutting across weight categories - yes, even women who are not overweight aren’t immune to this issue. This metabolic dysfunction sets off a chain reaction of hormonal imbalances that worsen PCOS symptoms. Let’s dive into how these disruptions intensify symptoms and complicate treatment.
How Insulin Resistance Drives PCOS Symptoms
When cells become less responsive to insulin, the pancreas compensates by overproducing it. This excess insulin fuels the ovaries to produce more androgens (male hormones) and reduces liver production of SHBG (sex hormone-binding globulin), which in turn increases free testosterone levels by 2–3 times.
The result? A cascade of symptoms that can be hard to miss: hirsutism (excess facial and body hair), acne, thinning scalp hair, and irregular or even absent menstrual cycles. Elevated androgens also interfere with ovulation, making conception more difficult - a challenge faced by the majority of women with PCOS. On top of that, insulin resistance encourages fat to accumulate around the abdomen, making weight loss frustratingly difficult despite efforts with diet and exercise.
But it doesn’t stop at reproductive symptoms. Insulin resistance significantly raises the risk of serious health conditions. Women with PCOS are 5–10 times more likely to develop type 2 diabetes and often show warning signs of cardiovascular disease, such as high LDL cholesterol, high triglycerides, and low HDL cholesterol. What’s particularly striking is that these risks persist even in women who are not obese, making it clear that tackling insulin resistance is key to managing PCOS effectively.
Why Insulin Resistance Is Difficult to Treat
While treatments like metformin can reduce insulin resistance markers like HOMA-IR by 10–30%, they come with notable challenges. For one, 20–30% of patients experience side effects like gastrointestinal discomfort, which can make sticking to the medication tough. On top of that, adherence to lifestyle changes often drops below 40% after just six months. And here’s the kicker: these traditional approaches don’t address gut microbiota imbalances, which play a role in insulin resistance for 60–80% of women with PCOS.
Even with standard treatments, only 40–60% of women see significant improvements in insulin resistance. To make matters more complicated, some hormone-based therapies can worsen metabolic problems rather than help. This has driven researchers to look at alternative options. One promising avenue? Synbiotics. These combine probiotics and prebiotics, boosting insulin sensitivity by up to 30% more than probiotics alone, with side effects like bloating affecting fewer than 10% of users.
How Synbiotics Help Manage PCOS
Emerging research suggests that synbiotics may offer a promising approach to managing insulin resistance in women with PCOS. Synbiotics combine probiotics - the beneficial bacteria that support gut health - with prebiotics, which serve as food for those bacteria. Together, they help create a healthier gut environment. This improved microbiome can produce short-chain fatty acids like butyrate, which reduce inflammation and improve how cells respond to insulin.
Synbiotics' Role in Gut Health and Insulin Sensitivity
Synbiotics work through multiple mechanisms. Prebiotics such as inulin encourage the growth of beneficial bacteria, increase microbial diversity, and strengthen the gut lining. A stronger gut lining can reduce intestinal permeability (commonly known as "leaky gut") and lower inflammation throughout the body. These changes make it easier for cells to absorb glucose, reducing insulin resistance - often measured by HOMA-IR scores.
Additionally, synbiotics can influence specific gut bacteria families like Ruminococcaceae, Lachnospiraceae, and Bacteroides. These bacteria play a role in regulating hormones tied to appetite and insulin signaling. Such gut-level changes provide the foundation for the clinical improvements seen in recent studies.
What the Research Says About Synbiotics for PCOS
A systematic review published in Nutrients examined controlled trials and found that synbiotic supplementation significantly improved insulin resistance in women with PCOS. The review highlighted reductions in HOMA-IR, fasting glucose, and fasting insulin levels - results that outperformed probiotics alone.
For example, one study reported that after 8 weeks of synbiotic use:
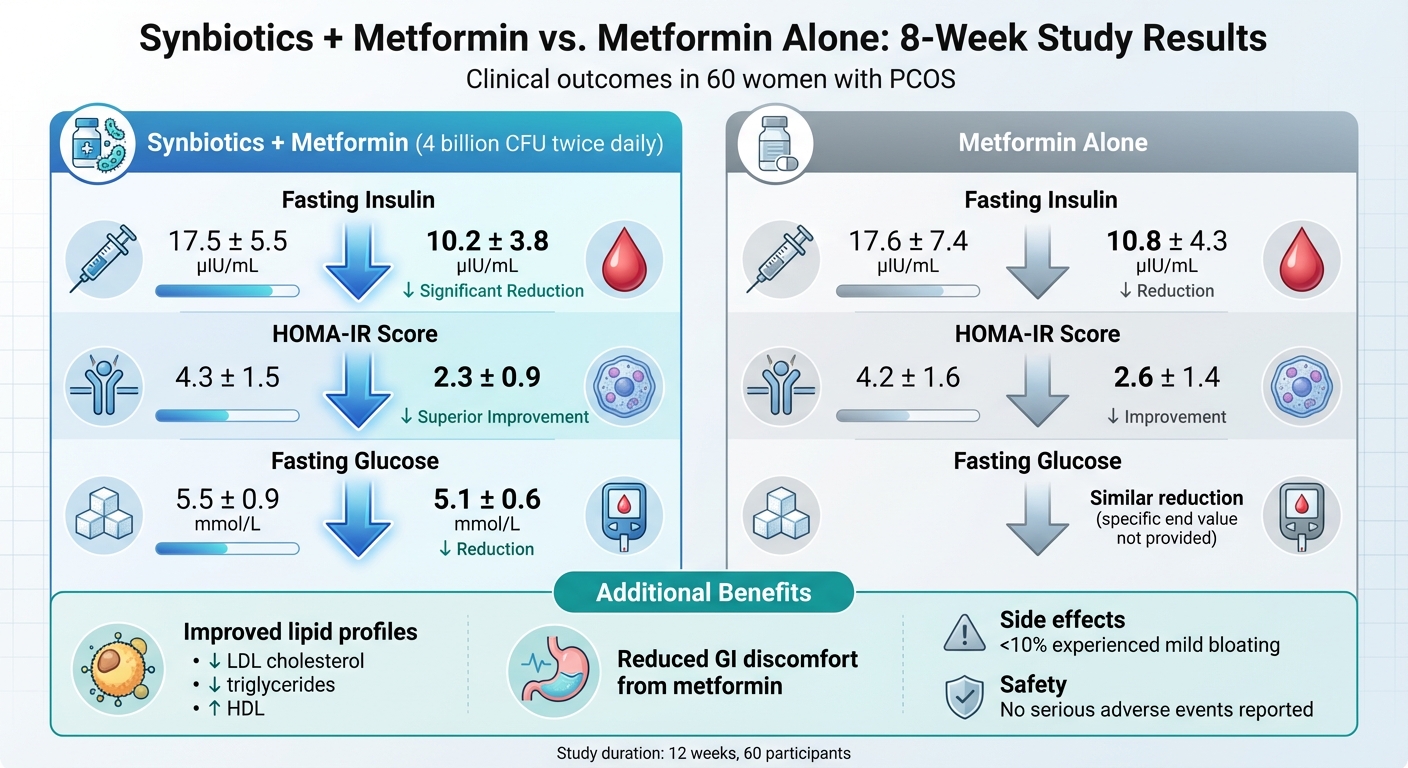
- Fasting glucose dropped from 5.5 ± 0.9 mmol/L to 5.1 ± 0.6 mmol/L.
- Fasting insulin levels decreased from 17.5 ± 5.5 µIU/mL to 10.2 ± 3.8 µIU/mL.
- HOMA-IR scores improved from 4.3 ± 1.5 to 2.3 ± 0.9.
Beyond blood sugar control, synbiotics have shown benefits for cholesterol and hormones. Studies report lower LDL cholesterol and triglycerides, a slight increase in HDL cholesterol (about 3.2 mg/dL), higher levels of sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG), and reduced free testosterone. Side effects were minimal, with fewer than 10% of participants experiencing mild bloating, and no serious adverse events were noted.
Which Synbiotic Strains and Doses Are Effective
Research indicates that multi-strain synbiotics containing Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains are particularly effective for addressing gut imbalances linked to insulin resistance in PCOS. The most successful regimens typically include at least 10⁹ colony-forming units (CFU) per day. A common protocol involves taking around 4 billion CFU twice daily, combined with prebiotics like inulin or resistant dextrin, for 8–12 weeks. When choosing a supplement, look for one that clearly lists the strains and provides the recommended dosage for the full treatment period.
sbb-itb-6dba428
Using Synbiotics with Standard PCOS Medications
For many women managing PCOS, metformin is a common choice to tackle insulin resistance. But what happens when you pair it with synbiotics? A 12-week study involving 60 women with PCOS found that adding synbiotics (4 billion CFU twice daily) to metformin significantly improved results. Fasting insulin levels dropped from 17.5 ± 5.5 to 10.2 ± 3.8 µIU/mL, and HOMA-IR scores improved from 4.3 ± 1.5 to 2.3 ± 0.9. In comparison, metformin alone reduced fasting insulin from 17.6 ± 7.4 to 10.8 ± 4.3 µIU/mL and HOMA-IR from 4.2 ± 1.6 to 2.6 ± 1.4.
How Synbiotics and Metformin Work Together
The combination of synbiotics and metformin tackles PCOS from two angles. Metformin improves insulin sensitivity, while synbiotics help restore healthy gut bacteria and reduce inflammation. Together, they not only enhance insulin sensitivity but also improve lipid profiles - lowering LDL cholesterol and triglycerides while boosting HDL levels. On top of that, synbiotics can help ease gastrointestinal discomfort by promoting a balanced gut environment.
How to Add Synbiotics to Your Treatment Plan
If you're considering adding synbiotics to your routine, here's a practical approach. Always consult your healthcare provider first. To minimize GI discomfort, try taking synbiotics in the morning and metformin later in the day. Look for a multi-strain synbiotic product containing Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium (around 4 billion CFU per dose) combined with a prebiotic like inulin. Use it consistently for 8–12 weeks, and monitor your progress with quarterly blood tests to check HOMA-IR, fasting glucose, and fasting insulin levels.
In addition to supplements, you can support your gut health by adding foods like yogurt with live cultures and inulin-rich options such as onions and garlic to your diet. This combined approach can help you get the most out of your treatment plan.
What This Means for Treatment and How Oana Health Can Help
Synbiotics vs Metformin for PCOS Insulin Resistance: 8-Week Clinical Results
Studies reveal that combining prescription treatments with gut health strategies can significantly improve insulin sensitivity for those managing PCOS. For instance, meta-analyses show that using synbiotics alongside standard care - like metformin - leads to greater reductions in fasting insulin levels, HOMA-IR scores, and triglycerides compared to using medication by itself. This combined approach delivers stronger metabolic benefits and sets the stage for integrated treatment options, which are now more accessible through telehealth services.
Oana Health's Treatments for Insulin Resistance
Oana Health provides prescription medications such as Oral Metformin ER ($22/month) and a Metformin & Spironolactone combination ($32/month). These are prescribed by licensed professionals and shipped directly to your home at no extra cost. These treatments are designed to address insulin resistance head-on, creating a solid foundation for pairing with gut health interventions.
For women who experience digestive discomfort from oral metformin, Oana Health also offers a Topical Metformin option starting at $89/month. One patient reported that the topical version resolved her gastrointestinal issues while still providing the same benefits. This improved tolerability helps ensure consistent treatment, which can amplify the positive effects of gut health strategies.
Why Personalized Treatment Plans Matter
Since PCOS symptoms can vary widely from person to person, tailoring treatment to each individual's gut microbiota and insulin sensitivity is critical. Oana Health's telehealth platform simplifies this process with a quick 5-minute online medical history intake, ensuring that treatment plans are customized to meet specific needs. By offering personalized care, these plans enhance how medications like Metformin ER work in tandem with gut health therapies, improving adherence and reducing side effects compared to one-size-fits-all approaches.
Research supports the idea that combining pharmacological treatments with microbiome-focused care delivers the best results. By addressing insulin resistance through medications and gut health strategies together, this comprehensive method tackles PCOS from multiple angles. Oana Health's user-friendly platform, complete with ongoing support and automatic refills, helps patients stay consistent with their personalized treatment plans, maximizing the effectiveness of their care.
Conclusion
Research indicates that synbiotics - combinations of probiotics and prebiotics - may help improve insulin resistance in women with PCOS. Studies consistently show improvements in key metabolic markers, especially when multi-strain formulas with prebiotic fibers like inulin are used over 8–12 weeks.
While the evidence is still developing, synbiotics seem most effective when paired with standard insulin-sensitizing treatments, such as metformin, rather than used alone. For instance, adding probiotics to metformin reduced fasting blood sugar levels from 5.5 ± 0.9 to 5.1 ± 0.6 mmol/L and fasting insulin from 17.5 ± 5.5 to 10.2 ± 3.8 µIU/mL, though the additional benefit over metformin alone was not statistically significant. Reviews suggest that combining gut health strategies with prescription medications may improve metabolic outcomes and potentially reduce side effects. These findings highlight the potential of integrating synbiotics into conventional treatments for a more tailored approach.
Given the variability in PCOS symptoms and treatment responses, personalized care is key. Oana Health’s telehealth platform simplifies this by offering evidence-based treatments for insulin resistance, such as Oral Metformin ER for $22/month, along with other combination options. These treatments are prescribed by licensed professionals and delivered to your door.
Before adding synbiotics to your routine, consult a healthcare provider familiar with PCOS. They can guide you in selecting a multi-strain formula containing Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium species with a prebiotic fiber like inulin. An 8–12 week trial is often recommended to track progress. Look for products with verified CFU counts and strains, and notify your provider of any new digestive symptoms. Trials have reported mild, temporary bloating in fewer than 10% of participants.
FAQs
How can synbiotics help with insulin resistance in women with PCOS?
Synbiotics may play a role in improving insulin resistance for women with PCOS by promoting a healthier gut microbiome. They help by balancing gut bacteria, reducing inflammation, and boosting the body’s ability to use insulin effectively. This can lead to better blood sugar regulation and a more balanced hormonal environment.
Studies indicate that these benefits might also ease some common PCOS symptoms, like weight gain and irregular periods, by targeting one of the underlying factors of the condition.
Can synbiotics alone treat insulin resistance in women with PCOS?
No, synbiotics are not viewed as a sole treatment for insulin resistance in women with PCOS. While studies indicate they can aid gut health and metabolic processes, their effectiveness is maximized when paired with other interventions like a balanced diet, regular exercise, and medical treatments recommended by a healthcare provider.
To effectively manage PCOS and insulin resistance, it’s essential to work with a licensed medical professional who can develop a treatment plan specifically tailored to your individual needs.
How can I choose the right synbiotic supplement to help manage PCOS and insulin resistance?
When choosing a synbiotic supplement to help manage PCOS and insulin resistance, prioritize products containing clinically researched strains that have demonstrated benefits for gut health and metabolic support. Opt for high-quality options without unnecessary fillers or additives to ensure you're getting the best results.
Don't forget to consult with a healthcare professional. They can provide personalized recommendations based on your unique health needs and goals, helping you select a supplement that aligns with your approach to managing PCOS symptoms effectively.
