Ultrasound Monitoring During Clomiphene Cycles
When you're taking Clomiphene to stimulate ovulation, ultrasound monitoring is essential for tracking progress and ensuring safety. Without ultrasounds, it's harder to determine if the treatment is working or to avoid complications like multiple pregnancies or ovarian hyperstimulation. Here's what you need to know:
- Clomiphene Citrate helps women with ovulation issues, especially those with PCOS, by stimulating egg release. Ovulation typically occurs 5–10 days after treatment.
- Ultrasounds track follicle growth, measure uterine lining thickness, and pinpoint the best time for conception or IUI.
- Monitoring helps adjust medication doses, avoid overstimulation, and reduce risks of thin uterine lining or multiple pregnancies.
Key ultrasound steps include:
- Baseline Scan (Cycle Days 2–4): Checks for ovarian cysts, pregnancy, and uterine abnormalities.
- Mid-Cycle Scans (Day 9 or 10): Monitor follicle size and endometrial lining.
- Final Scan Before Ovulation: Confirms follicle maturity and ideal timing for conception.
Ultrasounds ensure your treatment is safe, effective, and tailored to improve your chances of conception. They also help identify if changes, such as switching medications, are needed for better results.
TOP POST FROM 2025: A monitoring ultrasound (in this case, after clomid) helps us confirm how the
When Ultrasounds Are Performed During Clomiphene Cycles
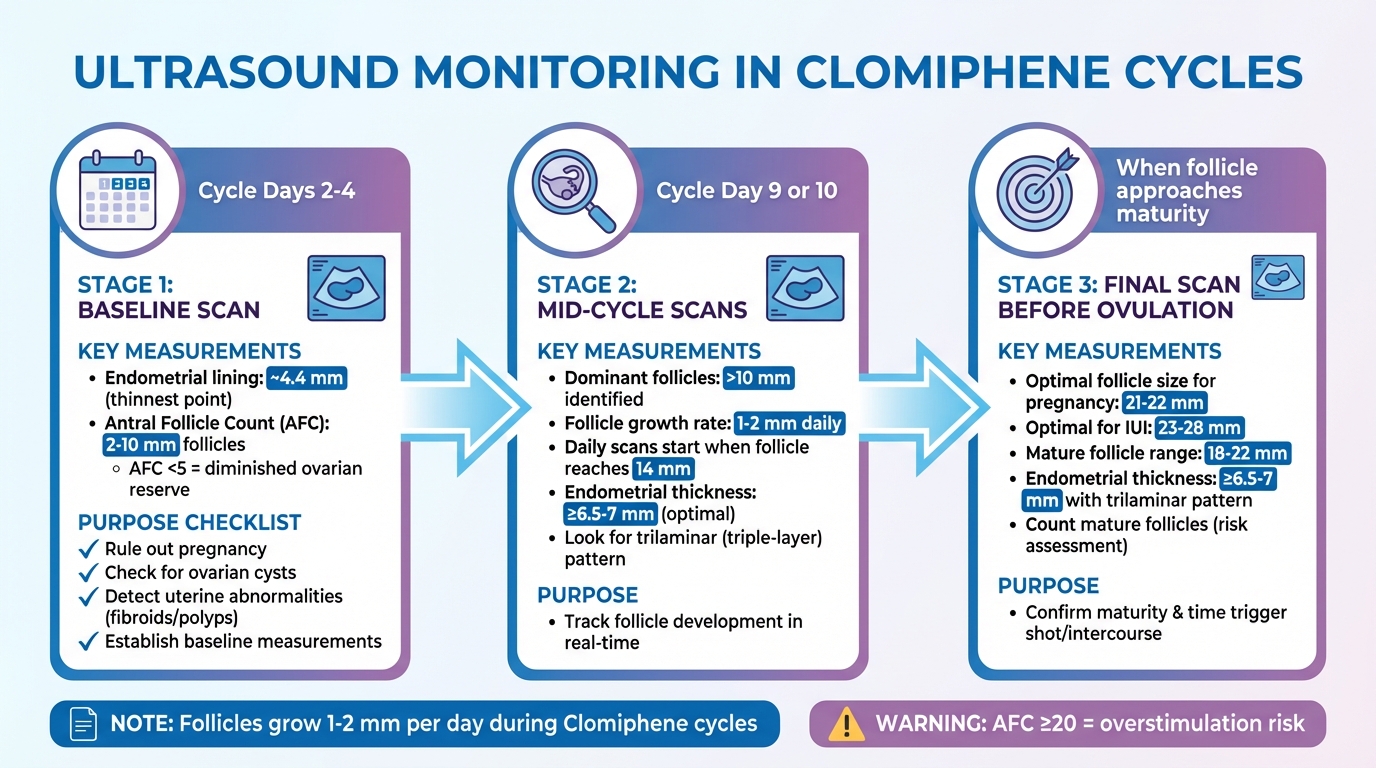
Ultrasound Monitoring Timeline During Clomiphene Cycles
Ultrasound scans play a crucial role during Clomiphene cycles, helping to confirm readiness, monitor follicle growth, and guide the timing for conception attempts.
Baseline Ultrasound Before Treatment Starts
The first ultrasound, known as the baseline scan, is typically scheduled between cycle days 2 and 4. This is when the endometrial lining is at its thinnest - averaging about 4.4 mm - and the ovaries are easiest to evaluate without interference from large cysts or remnants of the corpus luteum.
"Patients must be evaluated to exclude pregnancy, ovarian enlargement, or ovarian cyst formation between each treatment cycle." – StatPearls
This scan is key to ruling out potential issues, such as ovarian cysts unrelated to PCOS, an undetected pregnancy, or ovarian enlargement. It also includes an antral follicle count (AFC), which assesses ovarian reserve by counting follicles measuring 2–10 mm. An AFC below 5 often suggests a diminished ovarian reserve. Additionally, the scan checks for uterine abnormalities like fibroids or polyps, which could interfere with implantation, and establishes baseline measurements for ovarian volume and endometrial thickness.
Mid-Cycle Scans to Monitor Follicle Growth
After the baseline evaluation, mid-cycle ultrasounds are used to track follicle development in real time. These scans usually occur around cycle day 9 or 10. At this stage, dominant follicles larger than 10 mm are identified, and their growth is monitored. In Clomiphene cycles, follicles grow approximately 1–2 mm daily, slightly faster than the 1–1.4 mm growth seen in natural cycles.
Once a follicle reaches about 14 mm, daily ultrasounds are often performed to closely monitor its progress. These scans also evaluate the endometrial lining, as a preovulatory thickness of 6.5 to 7 mm or more is linked to higher pregnancy rates. Providers look for a trilaminar (triple-layer) pattern in the uterine lining, which indicates that it is primed for embryo implantation.
Final Scan Before Ovulation
The last ultrasound in the cycle confirms that the follicle has reached maturity and helps determine the optimal timing for intercourse or a trigger injection. For Clomiphene cycles, follicles measuring 21–22 mm are associated with higher chances of clinical pregnancy, while an ideal size for IUI cycles falls between 23–28 mm.
This final scan also counts the number of mature follicles, which is critical for assessing the likelihood of multiple pregnancies. Additionally, it measures the endometrial thickness and verifies the presence of the trilaminar pattern, ensuring conditions are favorable for conception before proceeding.
What Providers Evaluate During Ultrasound Scans
During an ultrasound, healthcare providers focus on key measurements that guide decisions about continuing the treatment cycle, adjusting medications, or timing conception efforts. These scans provide a real-time look at how your body is responding to Clomiphene therapy, helping to fine-tune the process for optimal outcomes.
Follicle Size and Development
One of the primary focuses during these scans is follicle size. Providers measure follicles by averaging two perpendicular diameters, and for those larger than 15 mm, they use three planes for accuracy. In Clomiphene cycles, follicles measuring between 21–22 mm are most strongly linked to successful pregnancies. Generally, a mature follicle ready for ovulation falls within the 18–22 mm range.
Clinicians also track the daily growth rate of follicles, which typically increases by 1–2 mm per day, to predict ovulation and plan for either intercourse or a trigger injection. Alongside size, the follicle's appearance is evaluated. Healthy follicles are round, smooth, and appear darker (hypoechoic) on the ultrasound screen, while irregularly shaped follicles with rough edges are less likely to ovulate.
These measurements are essential for tailoring medication dosages and determining the timing of key steps in the cycle.
Endometrial Thickness
The thickness of the uterine lining, or endometrium, is another critical factor. Providers measure the lining at its thickest point. A preovulatory thickness of 6.5–7 mm or more is linked to better pregnancy rates, while a lining thinner than 6 mm may reduce the chances of conception. Since Clomiphene can sometimes thin the lining due to its anti-estrogenic effects, this aspect is closely monitored.
Providers also assess the endometrial pattern. A "trilaminar" or triple-layered appearance - characterized by a darker (hypoechoic) endometrium with a bright central line - is a positive sign for implantation success and typically appears 5–6 days before ovulation. After ovulation, this pattern fades as the lining becomes more uniform and brighter, confirming ovulation has occurred.
This evaluation ensures the uterine environment is conducive to the goals of the treatment cycle.
Identifying Potential Problems
Ultrasounds also help detect potential issues that could interfere with the cycle. Baseline scans can reveal residual cysts or uterine abnormalities like fibroids or polyps, which may hinder implantation . If a functional cyst is found, treatment may be delayed until it resolves .
Mid-cycle scans are used to monitor for excessive follicle development. Too many mature follicles can increase the risk of multifetal pregnancies . Providers also watch for signs of ovarian hyperstimulation, which is indicated by an Antral Follicle Count of 20 or more. In such cases, the cycle may be canceled, intercourse may be discouraged, or follicle aspiration may be performed to reduce the number of mature eggs .
If the endometrial lining remains persistently thin (below 6–7 mm), providers may recommend supplements like oral, vaginal, or transdermal estradiol, though the effectiveness of this approach is still debated. Alternatively, they might consider switching to medications such as Tamoxifen or Letrozole in future cycles, as these drugs can have different effects on the uterine lining.
sbb-itb-6dba428
How Ultrasound Results Guide Treatment Decisions
Ultrasound plays a crucial role in shaping fertility treatments, offering real-time insights to fine-tune medication and schedules. These scans help tailor each step of the process to improve outcomes and ensure safety.
Adjusting Clomiphene Dosage
Ultrasound findings are key when adjusting Clomiphene treatment. If the initial 50 mg dose doesn’t stimulate follicle growth, the dose may be increased to 100 mg daily in the next cycle. However, if ovulation occurs but pregnancy doesn’t follow, increasing the dose further doesn’t improve results. As StatPearls explains, "If the patient ovulates during the first cycle but does not become pregnant, there is no advantage to increasing the dose in subsequent cycles".
Providers may also use lower starting doses or shorter treatment periods to minimize the risk of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) while still encouraging ovulation. If repeated scans show a thin endometrial lining (less than 6–7 mm), which can be a side effect of Clomiphene, the provider might switch to medications like Letrozole or Tamoxifen instead of increasing the Clomiphene dose.
Preventing Multiple Pregnancies and Overstimulation
Ultrasound monitoring is essential for managing risks, such as multiple pregnancies or overstimulation. For instance, if a woman under 40 has more than two mature follicles, the likelihood of a multifetal pregnancy increases. In such cases, providers may cancel the cycle, recommend avoiding timed intercourse or intrauterine insemination (IUI), or withhold the hCG trigger shot altogether.
An Antral Follicle Count of 20 or more can signal an "over-response", indicating a high risk for OHSS. Since OHSS can escalate quickly - sometimes within 24 hours - and become a medical emergency, early detection is critical. Providers also conduct pelvic exams or ultrasounds before starting a new cycle to ensure no ovarian enlargement or unresolved cysts from prior treatments. This careful monitoring ensures treatment proceeds safely and effectively.
Determining the Best Timing for Conception
Ultrasound results are invaluable for pinpointing the ideal time for conception. When follicles reach the optimal size, providers can schedule the hCG trigger shot, which typically induces ovulation within about 36 hours. This allows precise planning for either timed intercourse or IUI procedures.
An endometrial lining of at least 6.5–7 mm is considered ideal for implantation. In some cases, daily scans are used as follicles approach 16 mm to determine the exact timing for the trigger shot. Post-ovulation scans can confirm success by showing a collapsed dominant follicle and free fluid in the pouch of Douglas.
| Ultrasound Finding | Clinical Action |
|---|---|
| No dominant follicle growth | Increase dose for next cycle (50 mg to 100 mg) |
| Ovulation achieved, no pregnancy | Maintain current dose |
| More than 2 mature follicles | Cancel cycle or avoid timed intercourse/IUI |
| Pre-existing ovarian cyst | Delay treatment until cyst resolves |
| Endometrial lining below 6 mm | Switch to Letrozole or Tamoxifen |
At Oana Health, we integrate these ultrasound findings into every aspect of your treatment plan, ensuring a customized approach that prioritizes both safety and success.
Conclusion
Ultrasound monitoring transforms Clomiphene treatment into a tailored and precise approach. By tracking follicle growth and endometrial changes in real-time, healthcare providers can fine-tune dosing, identify the optimal window for conception, and address potential complications early. Research indicates that Clomiphene cycles result in a 68% ovulation rate and a 32% pregnancy rate, offering valuable benchmarks for adjusting treatment to balance effectiveness and safety.
This monitoring also plays a key role in ensuring safety. It helps providers detect the development of more than two mature follicles - an indicator of an increased risk for multiple pregnancies - and modify the treatment plan accordingly. Additionally, ultrasound can reveal Clomiphene’s anti-estrogenic effects on the uterine lining, which might necessitate switching to other medications. As noted by the Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects (DARE), "There is currently no basis for amending the evidence base (good‐practice points) used in the RCOG and NICE guidelines, which recommend the use of US to monitor the ovaries during stimulation with CC". This professional oversight not only improves success rates but also safeguards your health throughout the process.
For those managing PCOS or exploring fertility treatments, Oana Health provides telehealth services with licensed professionals who design personalized, evidence-based treatment plans. With medications delivered to your door and ongoing support, you can receive expert care without the inconvenience of traditional clinic visits.
Achieving successful ovulation and conception demands expert guidance and accurate monitoring - ultrasound is the tool that makes it possible.
FAQs
Why is ultrasound monitoring necessary during Clomiphene cycles?
Ultrasound monitoring plays a key role during Clomiphene Citrate (Clomid) cycles, as it helps track the development of ovarian follicles. This ensures ovulation is timed precisely, which can boost the likelihood of conception. By identifying the dominant follicle as it nears the optimal size (18–22 mm), healthcare providers can determine the best time for a trigger shot or intercourse.
Ultrasounds also keep an eye on the number of developing follicles, helping to minimize risks like multiple pregnancies or ovarian overstimulation. In addition, they offer important insights that allow for adjustments to Clomiphene dosages in future cycles, ensuring the treatment remains both safe and effective. Most clinics typically schedule ultrasounds around days 10–12 of the cycle, with follow-ups every 2–3 days until the follicles are ready.
For those using telehealth services, Oana Health integrates ultrasound appointments into its tailored Clomiphene treatment plans, providing accessible and closely monitored care for women managing PCOS or ovulatory disorders.
How is ultrasound used to monitor follicle development during a Clomiphene cycle?
Ultrasound is an essential tool for tracking follicle development during a Clomiphene (Clomid) cycle, ensuring the treatment is both effective and safe. Here’s how the process typically unfolds:
- Baseline scan: Before starting Clomiphene, a transvaginal ultrasound is performed to evaluate ovarian size, count antral follicles, and measure the thickness of the endometrial lining. This sets the stage for monitoring progress throughout the cycle.
- Mid-cycle scans: Around days 7–9 of treatment, another scan is done to monitor follicular growth and confirm that the ovaries are responding as expected to the medication.
- Pre-ovulation scan: Once a dominant follicle grows to about 18–22 mm, a final ultrasound is conducted to verify ovulation readiness. At this point, doctors may plan the next steps, such as administering an hCG trigger shot or timing natural ovulation.
These ultrasounds not only help fine-tune ovulation induction but also ensure the endometrial lining is prepared for implantation. Additionally, they play a critical role in minimizing risks, like the possibility of multiple pregnancies.
How does ultrasound monitoring guide treatment during Clomiphene cycles?
Ultrasound monitoring is a crucial part of Clomiphene Citrate (Clomid) cycles, enabling healthcare providers to closely observe how your ovaries respond to the medication. These scans allow clinicians to measure the size, number, and growth of ovarian follicles - key indicators of how well the treatment is progressing.
With the information gathered from ultrasounds, your provider can fine-tune your Clomiphene dose for the next cycle if the follicles are too small (less than 16 mm). They can also use this data to schedule ovulation-related activities, such as intercourse or intrauterine insemination (IUI), when a follicle reaches its ideal size of 18–22 mm. In cases where multiple mature follicles are identified, steps may be taken to lower the risk of multiple pregnancies. This might include reducing the medication dose, administering a trigger shot, or even canceling the cycle if needed.
The real-time insights from ultrasound scans allow for personalized adjustments, ensuring safer and more effective treatment. Oana Health incorporates this evidence-based monitoring into its Clomiphene programs, delivering care tailored to the specific needs of each patient.
